Redox Signaling Mediated by Thioredoxin and Glutathione Systems in the Central Nervous System
- PMID: 28443683
- PMCID: PMC5649126
- DOI: 10.1089/ars.2016.6925
Redox Signaling Mediated by Thioredoxin and Glutathione Systems in the Central Nervous System
Abstract
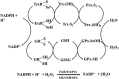
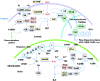
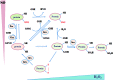
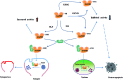
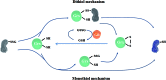
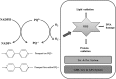
Significance: The thioredoxin (Trx) and glutathione (GSH) systems play important roles in maintaining the redox balance in the brain, a tissue that is prone to oxidative stress due to its high-energy demand. These two disulfide reductase systems are active in various areas of the brain and are considered to be critical antioxidant systems in the central nervous system (CNS). Various neuronal disorders have been characterized to have imbalanced redox homeostasis. Recent Advances: In addition to their detrimental effects, recent studies have highlighted that reactive oxygen species/reactive nitrogen species (ROS/RNS) act as critical signaling molecules by modifying thiols in proteins. The Trx and GSH systems, which reversibly regulate thiol modifications, regulate redox signaling involved in various biological events in the CNS.
Critical issues: In this review, we focus on the following: (i) how ROS/RNS are produced and mediate signaling in CNS; (ii) how Trx and GSH systems regulate redox signaling by catalyzing reversible thiol modifications; (iii) how dysfunction of the Trx and GSH systems causes alterations of cellular redox signaling in human neuronal diseases; and (iv) the effects of certain small molecules that target thiol-based signaling pathways in the CNS.
Future directions: Further study on the roles of thiol-dependent redox systems in the CNS will improve our understanding of the pathogenesis of many human neuronal disorders and also help to develop novel protective and therapeutic strategies against neuronal diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 27, 989-1010.
Keywords: CNS; glutaredoxin; glutathione; redox signaling; thiol-targeted compounds; thioredoxin.
Figures
References
-
- Aberg F, Appelkvist EL, Dallner G, and Ernster L. Distribution and redox state of ubiquinones in rat and human tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys 295: 230–234, 1992 - PubMed
-
- Akterin S, Cowburn RF, Miranda-Vizuete A, Jimenez A, Bogdanovic N, Winblad B, and Cedazo-Minguez A. Involvement of glutaredoxin-1 and thioredoxin-1 in beta-amyloid toxicity and Alzheimer's disease. Cell Death Differ 13: 1454–1465, 2006 - PubMed
-
- Alehagen U. and Aaseth J. Selenium and coenzyme Q10 interrelationship in cardiovascular diseases—a clinician's point of view. J Trace Elem Med Biol 31: 157–162, 2015 - PubMed
-
- Alehagen U, Johansson P, Bjornstedt M, Rosen A, and Dahlstrom U. Cardiovascular mortality and N-terminal-proBNP reduced after combined selenium and coenzyme Q10 supplementation: a 5-year prospective randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial among elderly Swedish citizens. Int J Cardiol 167: 1860–1866, 2013 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

