Efficacy of everolimus plus octreotide LAR in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumor and carcinoid syndrome: final overall survival from the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 RADIANT-2 study
- PMID: 28444114
- PMCID: PMC7360141
- DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdx193
Efficacy of everolimus plus octreotide LAR in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumor and carcinoid syndrome: final overall survival from the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 RADIANT-2 study
Erratum in
-
Efficacy of everolimus plus octreotide LAR in patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumor and carcinoid syndrome: final overall survival from the randomized, placebo-controlled phase 3 RADIANT-2 study.Ann Oncol. 2019 Dec 1;30(12):2010. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdz222. Ann Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31406974 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: In the phase 3 RADIANT-2 study, everolimus plus octreotide long-acting repeatable (LAR) showed improvement of 5.1 months in median progression-free survival versus placebo plus octreotide LAR among patients with advanced neuroendocrine tumors associated with carcinoid syndrome. The progression-free survival P-value was marginally above the prespecified threshold for statistical significance. Here, we report final overall survival (OS) and key safety update from RADIANT-2.
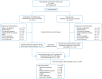
Patients and methods: The RADIANT-2 trial compared everolimus (10 mg/day, orally; n = 216) versus placebo (n = 213), both in conjunction with octreotide LAR (30 mg, intramuscularly, every 28 days). Patients, unblinded at the time of progression or after end of double-blind core phase following primary analysis, were offered open-label everolimus with octreotide LAR (open-label phase). In the open-label phase, patients had similar safety and efficacy assessments as those in the core phase. For OS, hazard ratios (HRs) with 95% CIs using unadjusted Cox model and a Cox model adjusted for prespecified baseline covariates were calculated.
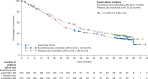
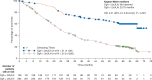
Results: A total of 170 patients received open-label everolimus (143 crossed over from the placebo arm; 27 in the everolimus arm continued to receive the same treatment after unblinding). The median OS (95% CI) after 271 events was 29.2 months (23.8-35.9) for the everolimus arm and 35.2 months (30.0-44.7) for the placebo arm (HR, 1.17; 95% CI, 0.92-1.49). HR adjusted for baseline covariates was 1.08 (95% CI, 0.84-1.38). The most frequent drug-related grade 3 or 4 AEs reported during the open-label phase were diarrhea (5.3%), fatigue (4.7%), and stomatitis (4.1%). Deaths related to pulmonary or cardiac failure were observed more frequently in the everolimus arm.
Conclusion: No significant difference in OS was observed for the everolimus plus octreotide LAR and placebo plus octreotide LAR arms of the RADIANT-2 study, even after adjusting for imbalances in the baseline covariates.
Clinical trial number: NCT00412061, www.clinicaltrials.gov.
Keywords: carcinoid syndrome; everolimus; neuroendocrine tumors; overall survival.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society for Medical Oncology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Yao J.C., Hassan M., Phan A. One hundred years after "carcinoid": epidemiology of and prognostic factors for neuroendocrine tumors in 35,825 cases in the United States. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:3063–3072. - PubMed
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Clinical practice guideline in oncology. Neuroendocrine tumors version 2. 2014; http://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/neuroendocrine.pdf (3 January 2017, last date accessed).
-
- Pavel M.E., Hainsworth J.D., Baudin E. Everolimus plus octreotide long-acting repeatable for the treatment of advanced neuroendocrine tumours associated with carcinoid syndrome (RADIANT-2): a randomised, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study. Lancet. 2011;378:2005–2012. - PubMed
-
- Therasse P., Arbuck S.G., Eisenhauer E.A. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment Of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000;92:205–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

