Preclinical Evidence That 5-HT1B Receptor Agonists Show Promise as Medications for Psychostimulant Use Disorders
- PMID: 28444326
- PMCID: PMC5570061
- DOI: 10.1093/ijnp/pyx025
Preclinical Evidence That 5-HT1B Receptor Agonists Show Promise as Medications for Psychostimulant Use Disorders
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018 Oct 1;21(10):978. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy077. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30184136 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
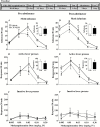
Background: 5-HT1B receptor agonists enhance cocaine intake during daily self-administration sessions but decrease cocaine intake when tested after prolonged abstinence. We examined if 5-HT1B receptor agonists produce similar abstinence-dependent effects on methamphetamine intake.
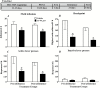
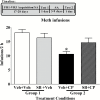
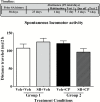
Methods: Male rats were trained to self-administer methamphetamine (0.1 mg/kg, i.v.) on low (fixed ratio 5 and variable ratio 5) and high (progressive ratio) effort schedules of reinforcement until intake was stable. Rats were then tested for the effects of the selective 5-HT1B receptor agonist, CP 94,253 (5.6 or 10 mg/kg), or the less selective but clinically available 5-HT1B/1D receptor agonist, zolmitriptan (10 mg/kg), on methamphetamine self-administration both before and after a 21-day forced abstinence period during which the rats remained in their home cages.
Results: The inverted U-shaped, methamphetamine dose-response function for intake on the fixed ratio 5 schedule was shifted downward by CP 94,253 both before and after abstinence. The CP 94,253-induced decrease in methamphetamine intake was replicated in rats tested on a variable ratio 5 schedule, and the 5-HT1B receptor antagonist SB 224,289 (10 mg/kg) reversed this effect. CP 94,253 also attenuated methamphetamine intake on a progressive ratio schedule both pre- and postabstinence. Similarly, zolmitriptan attenuated methamphetamine intake on a variable ratio 5 schedule both pre- and postabstinence, and the latter effect was sustained after each of 2 more treatments given every 2 to 3 days prior to daily sessions.
Conclusions: Unlike the abstinence-dependent effect of 5-HT1B receptor agonists on cocaine intake reported previously, both CP 94,253 and zolmitriptan decreased methamphetamine intake regardless of abstinence. These findings suggest that 5-HT1B receptor agonists may have clinical efficacy for psychostimulant use disorders.
Keywords: CP 94,253; addiction; methamphetamine; rodent; zolmitriptan.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of CINP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological evidence for an abstinence-induced switch in 5-HT1B receptor modulation of cocaine self-administration and cocaine-seeking behavior.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014 Mar 19;5(3):168-76. doi: 10.1021/cn400155t. Epub 2014 Jan 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 24369697 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of serotonin 5-HT1B receptor ligands on the cocaine- and food-maintained self-administration in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2007 Mar 22;559(2-3):165-72. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.12.012. Epub 2007 Jan 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17291490
-
5-HT1B receptor agonist attenuates cocaine self-administration after protracted abstinence and relapse in rats.J Psychopharmacol. 2021 Oct;35(10):1216-1225. doi: 10.1177/02698811211019279. Epub 2021 May 28. J Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34049460
-
Dopamine D3 and 5-HT1B receptor dysregulation as a result of psychostimulant intake and forced abstinence: Implications for medications development.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt B(0 0):301-19. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.08.014. Epub 2013 Aug 23. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23973315 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuropsychotoxicity of abused drugs: effects of serotonin receptor ligands on methamphetamine- and cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice.J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Jan;106(1):15-21. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fm0070121. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18198473 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of a 5-HT1B Receptor Agonist on Locomotion and Reinstatement of Cocaine-Conditioned Place Preference after Abstinence from Repeated Injections in Mice.Front Syst Neurosci. 2017 Oct 10;11:73. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2017.00073. eCollection 2017. Front Syst Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 29066957 Free PMC article.
-
5-HT1B receptor agonist enhances breakpoint for cocaine on a progressive ratio (PR) schedule during maintenance of self-administration in female rats but reduces breakpoint for sucrose.Front Behav Neurosci. 2022 Nov 1;16:1020146. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2022.1020146. eCollection 2022. Front Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36386780 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Cloning and Functional Characterization of Three 5-HT Receptor Genes (HTR1B, HTR1E, and HTR1F) in Chickens.Genes (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;12(6):891. doi: 10.3390/genes12060891. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207786 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahmed SH, Koob GF (1997) Cocaine- but not food-seeking behavior is reinstated by stress after extinction. Pharmacol 132:289–295. - PubMed
-
- Azzaro AJ, Rutledge CO (1973) Selectivity of release of norepinephrine, dopamine, and 5-hydroxytryptamine by amphetamine in various regions of rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 22:2801–2813. - PubMed
-
- Barnes NM, Neumaier JF (2011) Neuronal 5-HT receptors and SERT. Tocris Bioscience Review 1–16.
-
- Brown JM, Hanson GR, Fleckenstein AE (2001) Regulation of the vesicular monoamine transporter-2: a novel mechanism for cocaine and other psychostimulants. J Pharm Exp Ther 296:762–767 - PubMed
-
- Bruinvels AT, Landwehrmeyer B, Gustafson EL, Durkin MM, Mengod G, Branchek TA, Hoyer D, Palacios JM (1994) Localization of 5-HT1B, 5-HT1Da, 5-HT1E, and 5-HT1F receptor messenger RNA in rodent and primate brain. Neuropharmacol 33:367–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

