WBP2NL/PAWP mRNA and protein expression in sperm cells are not related to semen parameters, fertilization rate, or reproductive outcome
- PMID: 28444612
- PMCID: PMC5445044
- DOI: 10.1007/s10815-017-0902-x
WBP2NL/PAWP mRNA and protein expression in sperm cells are not related to semen parameters, fertilization rate, or reproductive outcome
Abstract
Purpose: WBP2NL/PAWP, a protein found in the post-acrosomal region of mammalian spermatozoa, has been proposed as a sperm-borne oocyte-activating factor (SOAF) contributing to Ca2+ release within the oocyte and subsequent fertilization and embryo development. However, its relevance as either a diagnostic or a prognostic marker of fertilization failure has been questioned in the recent literature. We analyzed WBP2NL/PAWP gene and protein expression level and localization in patients without previous intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles in order to assess its association with both sperm characteristics and ability to fertilize.
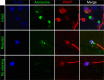
Methods: Raw frozen-thawed semen samples from 33 couples referred for oocyte donation were included in the study during 2015. Relative protein expression versus α-tubulin (western blot, WB), proportion of post-acrosomal WBP2NL/PAWP-positive spermatozoa over the total number of sperm cells (immunofluorescence), and WBP2NL/PAWP gene expression (RT-qPCR) were analyzed and correlated with semen analysis parameters (number, motility, and morphology) and with reproductive outcomes.
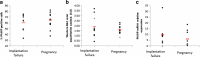
Results: WBP2NL/PAWP protein was expressed in all samples with high variability: relative protein expression (1.77 ± 0.8, range [0.4-3.7]), proportion of positive cells (49.6% ± 16.1, range [22-89]), and relative gene expression (7.3 ± 8.2). No significant correlation (R 2 < 0.1) was found between gene and protein expression, neither between WBP2NL/PAWP gene or protein expression, and fertilization rate or other reproductive outcomes (i.e., pregnancy). In contrast, we found significant correlation between sperm morphology and WBP2NL/PAWP semiquantitative analysis in WB (r = -0.42, p < 0.05) and for sperm motility and WBP2NL/PAWP expression in IF (r = 0.52, p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Taken into account that WBP2NL/PAWP gene and protein levels and distribution did not correlate with fertilization rates, this study questions the interest of WBP2NL/PAWP protein and gene expression analysis in sperm cells as a prognostic factor for the outcome of ICSI cycles. Larger studies focusing on WBP2NL/PAWP protein and gene expression are needed in order to evaluate the role of WBP2NL/PAWP as a prognostic factor for ART.
Keywords: Fertilization; Gene expression; ICSI; Oocyte donation; Sperm; WBP2NL/PAWP.
Conflict of interest statement
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all the couples involved in the study.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committees and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its subsequent amendments. This study has been performed per Good Clinical Practice (CPMP/ICH/ 135/95). The protocol was approved by the local Ethical Committee for Clinical Research.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yeste M, Fernandez-Novell JM, Ramio-Lluch L, Estrada E, Rocha LG, Cebrian-Perez JA, et al. Intracellular calcium movements of boar spermatozoa during ‘in vitro’ capacitation and subsequent acrosome exocytosis follow a multiple-storage place, extracellular calcium-dependent model. Andrology. 2015;3(4):729–747. doi: 10.1111/andr.12054. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Saunders CM, Larman MG, Parrington J, Cox LJ, Royse J, Blayney LM, et al. PLC zeta: a sperm-specific trigger of Ca(2+) oscillations in eggs and embryo development. Development. 2002;129(15):3533–3544. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

