Hematologic, hepatic, and renal function changes in hospitalized patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
- PMID: 28444873
- PMCID: PMC7165514
- DOI: 10.1111/ijlh.12620
Hematologic, hepatic, and renal function changes in hospitalized patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus
Abstract
Background: There are no longitudinal data on the changes in hematologic, hepatic, and renal function findings in patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) infection.
Methods: This is a retrospective cohort study of 16 MERS-CoV patients, to describe the hematological, hepatic, and renal findings of patients with MERS-CoV.
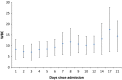
Results: During the 21 days of observation, there was no significant change in the hepatic panel or creatinine tests. There was a significant increase in the mean ± SD of the white blood cell count from 8.3 ± 4.6 to 14.53 ± 7 (P value = 0.001) and an increase in mean ± SD of the absolute neutrophil count from 6.33 ± 4.2 to 12 ± 5.5 (P value = 0.015). Leukocytosis was observed in 31% (5/16) of the patients on day 1 and in 80% (4/5) on day 21. Transient leukopenia developed in 6% (1/16) of the patients on day 1 and in 13% (1/8) on day 8. None of the patients had neutropenia. Lymphopenia was a prominent feature with a rate of 44% (7/16) of the patients on day 1 and 60% (3/5) on day 21. Lymphocytosis was not a feature of MERS-CoV infection. Thrombocytopenia developed in 31% (5/16) of the patients on day 1 and 40% (2/5) on day 21. Thrombocytosis was not a prominent feature and was observed in 6% (1/16) of the patients on day 1 and 17% (1/6) on day 9.
Conclusions: Patients with MERS-CoV infection showed variable hematologic parameters over time. Lymphocytosis and neutropenia were not features of MERS-CoV infection.
Keywords: Middle East respiratory syndrome; biochemical characteristics; hematologic changes.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zaki AM, van Boheemen S, Bestebroer TM, Osterhaus ADME, Fouchier RAM. Isolation of a novel coronavirus from a man with pneumonia in Saudi Arabia. N Engl J Med 2012;367:1814–20. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS‐CoV) ‐ Saudi Arabia. Disease outbreak news, 6 July 2016. Available at: http://www.who.int/csr/don/06-july-2016-mers-saudiarabia/en/. Accessed October 10, 2016.
-
- Arabi YM, Arifi AA, Balkhy HH, Najm H, Aldawood AS, Ghabashi A, Hawa H, Alothman A, Khaldi A, Al Raiy B. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus infection. Ann Intern Med 2014;160:389–97. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

