Autophagy and mitophagy in the context of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
- PMID: 28445146
- PMCID: PMC5542301
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16944
Autophagy and mitophagy in the context of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity
Abstract
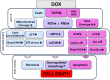
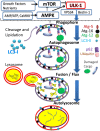
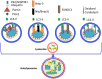
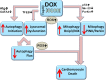
Doxorubicin (Dox) is a cytotoxic drug widely incorporated in various chemotherapy protocols. Severe side effects such as cardiotoxicity, however, limit Dox application. Mechanisms by which Dox promotes cardiac damage and cardiomyocyte cell death have been investigated extensively, but a definitive picture has yet to emerge. Autophagy, regarded generally as a protective mechanism that maintains cell viability by recycling unwanted and damaged cellular constituents, is nevertheless subject to dysregulation having detrimental effects for the cell. Autophagic cell death has been described, and has been proposed to contribute to Dox-cardiotoxicity. Additionally, mitophagy, autophagic removal of damaged mitochondria, is affected by Dox in a manner contributing to toxicity. Here we will review Dox-induced cardiotoxicity and cell death in the broad context of the autophagy and mitophagy processes.
Keywords: anthracyclines; heart failure; impaired autophagy and mitophagy; lysosomal dysfunction; oncocardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lipshultz SE, Miller TL, Lipsitz SR, Neuberg DS, Dahlberg SE, Colan SD, Silverman LB, Henkel JM, Franco VI, Cushman LL, Asselin BL, Clavell LA, Athale U, et al. Continuous Versus Bolus Infusion of Doxorubicin in Children With ALL: Long-term Cardiac Outcomes. Pediatrics. 2012;130:1003–11. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-0727. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lipshultz SE, Scully RE, Lipsitz SR, Sallan SE, Silverman LB, Miller TL, Barry EV, Asselin BL, Athale U, Clavell LA, Larsen E, Moghrabi A, Samson Y, et al. Assessment of dexrazoxane as a cardioprotectant in doxorubicin-treated children with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukaemia: long-term follow-up of a prospective, randomised, multicentre trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010;11:950–61. doi: 10.1016/s1470-2045(10)70204-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lipshultz SE, Miller TL, Scully RE, Lipsitz SR, Rifai N, Silverman LB, Colan SD, Neuberg DS, Dahlberg SE, Henkel JM, Asselin BL, Athale UH, Clavell LA, et al. Changes in cardiac biomarkers during doxorubicin treatment of pediatric patients with high-risk acute lymphoblastic leukemia: associations with long-term echocardiographic outcomes. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30:1042–9. doi: 10.1200/jco.2010.30.3404. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

