PKC and CaMK-II inhibitions coordinately rescue ischemia-induced GABAergic neuron dysfunction
- PMID: 28445148
- PMCID: PMC5503615
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16947
PKC and CaMK-II inhibitions coordinately rescue ischemia-induced GABAergic neuron dysfunction
Abstract
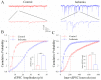
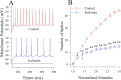
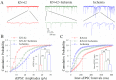
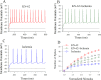
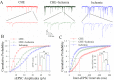
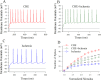
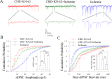
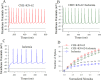
Cerebral ischemia leads to neuronal death for stroke, in which the imbalance between glutamatergic neurons and GABAergic neurons toward neural excitotoxicity is presumably involved. GABAergic neurons are vulnerable to pathological factors and impaired in an early stage of ischemia. The rescue of GABAergic neurons is expected to be the strategy to reserve ischemic neuronal impairment. As protein kinase C (PKC) and calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMK-II) are activated during ischemia, we have investigated whether the inhibitions of these kinases rescue the ischemic impairment of cortical GABAergic neurons. The functions of GABAergic neurons were analyzed by whole-cell recording in the cortical slices during ischemia and in presence of 1-[N,O-bis(5-isoquinolinesulfonyl)-N-methyl-L-tyrosyl]-4-phenylpiperazine (CaMK-II inhibitor) and chelerythrine chloride (PKC inhibitor). Our results indicate that PKC inhibitor or CaMK-II inhibitor partially prevents ischemia-induced functional deficits of cortical GABAergic neurons. Moreover, the combination of PKC and CaMK-II inhibitors synergistically reverses this ischemia-induced deficit of GABAergic neurons. One of potential therapeutic strategies for ischemic stroke may be to rescue the ischemia-induced deficit of cortical GABAergic neurons by inhibiting PKC and CaMK-II.
Keywords: GABA; PKC and CaMK-II; ischemia; neuron; synapse.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
All authors declare no competing interest. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Candelario-Jalil E. Injury and repair mechanisms in ischemic stroke: considerations for the development of novel neurotherapeutics. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2009;10:644–54. - PubMed
-
- Metha SL, Manhas N, Raghubir R. Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Research Review. 2007;54:34–66. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz-Bloom RD, Sah R. r-aminobutyric acid A neurotransmission and cerebral ischemia. Journal of neurochemistry. 2001;77:353–71. - PubMed
-
- Taoufik E, Probert L. Ischemic neuronal damage. Current Pharm Des. 2008;14:3565–73. - PubMed
-
- Welsh JP, Yuen G, Placantonkis DG, Yu TQ, Haiss F, O'Heaen E, Molliver ME, Aicher SA. Why do Purkinje cells die so easily after global brain ischemia? Aldolase C, EAAT4, and the cerebellar contribution to posthypoxic myoclonus. Advanced Neurology. 2002;89:331–59. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

