Renal vascular calcification and response to renal nerve denervation in resistant hypertension
- PMID: 28445258
- PMCID: PMC5413223
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006611
Renal vascular calcification and response to renal nerve denervation in resistant hypertension
Abstract
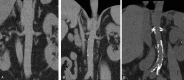
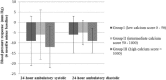
Renal sympathetic nerve denervation (RDN) is accepted as a treatment option for patients with resistant hypertension. However, results on decline in ambulatory blood pressure (BP) measurement (ABPM) are conflicting. The high rate of nonresponders may be related to increased systemic vascular stiffness rather than sympathetic overdrive. A single center, prospective registry including 26 patients with treatment resistant hypertension who underwent RDN at the Isala Hospital in the Netherlands. Renal perivascular calcium scores were obtained from noncontrast computed tomography scans. Patients were divided into 3 groups based on their calcium scores (group I: low 0-50, group II: intermediate 50-1000, and group III: high >1000). The primary end point was change in 24-hour ABPM at 6 months follow-up post-RDN compared to baseline. Seven patients had low calcium scores (group I), 13 patients intermediate (group II), and 6 patients had high calcium scores (group III). The groups differed significantly at baseline in age and baseline diastolic 24-hour ABPM. At 6-month follow-up, no difference in 24-hour systolic ABPM response was observed between the 3 groups; a systolic ABPM decline of respectively -9 ± 12, -6 ± 12, -12 ± 10 mm Hg was found. Also the decline in diastolic ambulatory and office systolic and diastolic BP was not significantly different between the 3 groups at follow-up. Our preliminary data showed that the extent of renal perivascular calcification is not associated with the ABPM response to RDN in patients with resistant hypertension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no funding and conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Mahfoud F, Luscher TF, Andersson B, et al. Expert consensus document from the European Society of Cardiology on catheter-based renal denervation. Eur Heart J 2013;34:2149–57. - PubMed
-
- O’Brien E, Parati G, Stergiou G, et al. European Society of Hypertension position paper on ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. J Hypertens 2013;31:1731–68. - PubMed
-
- Bakris GL, Townsend RR, Liu M, et al. Impact of renal denervation on 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure: results from SYMPLICITY HTN-3. J Am Coll Cardiol 2014;64:1071–8. - PubMed
-
- Esler MD, Krum H, Sobotka PA, et al. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension (The Symplicity HTN-2 Trial): a randomized controlled trial. Lancet 2010;376:1903–9. - PubMed
-
- Krum H, Schlaich MP, Sobotka PA, et al. Percutaneous renal denervation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension: final 3-year report of the Symplicity HTN-1 study. Lancet 2014;383:622–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

