Floor-plate-derived netrin-1 is dispensable for commissural axon guidance
- PMID: 28445456
- PMCID: PMC5438598
- DOI: 10.1038/nature22331
Floor-plate-derived netrin-1 is dispensable for commissural axon guidance
Abstract
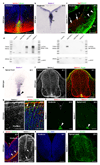
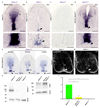
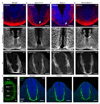
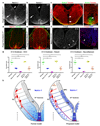
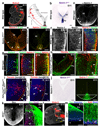
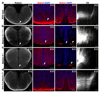
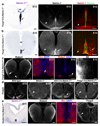
Netrin-1 is an evolutionarily conserved, secreted extracellular matrix protein involved in axon guidance at the central nervous system midline. Netrin-1 is expressed by cells localized at the central nervous system midline, such as those of the floor plate in vertebrate embryos. Growth cone turning assays and three-dimensional gel diffusion assays have shown that netrin-1 can attract commissural axons. Loss-of-function experiments further demonstrated that commissural axon extension to the midline is severely impaired in the absence of netrin-1 (refs 3, 7, 8, 9). Together, these data have long supported a model in which commissural axons are attracted by a netrin-1 gradient diffusing from the midline. Here we selectively ablate netrin-1 expression in floor-plate cells using a Ntn1 conditional knockout mouse line. We find that hindbrain and spinal cord commissural axons develop normally in the absence of floor-plate-derived netrin-1. Furthermore, we show that netrin-1 is highly expressed by cells in the ventricular zone, which can release netrin-1 at the pial surface where it binds to commissural axons. Notably, Ntn1 deletion from the ventricular zone phenocopies commissural axon guidance defects previously described in Ntn1-knockout mice. These results show that the classical view that attraction of commissural axons is mediated by a gradient of floor-plate-derived netrin-1 is inaccurate and that netrin-1 primarily acts locally by promoting growth cone adhesion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Serafini T, et al. The netrins define a family of axon outgrowth-promoting proteins homologous to C. elegans UNC-6. Cell. 1994;78:409–424. - PubMed
-
- Ishii N, Wadsworth WG, Stern BD, Culotti JG, Hedgecock EM. UNC-6, a laminin-related protein, guides cell and pioneer axon migrations in C. elegans. Neuron. 1992;9:873–881. - PubMed
-
- Mitchell KJ, et al. Genetic analysis of Netrin genes in Drosophila: Netrins guide CNS commissural axons and peripheral motor axons. Neuron. 1996;17:203–215. - PubMed
-
- Kennedy TE, Serafini T, de la Torre J, Tessier-Lavigne M. Netrins are diffusible chemotropic factors for commissural axons in the embryonic spinal cord. Cell. 1994;78:425–435. - PubMed
-
- Ming GL, et al. cAMP-dependent growth cone guidance by netrin-1. Neuron. 1997;19:1225–1235. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

