Neural correlates of evoked phantom limb sensations
- PMID: 28445695
- PMCID: PMC5437955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsycho.2017.04.009
Neural correlates of evoked phantom limb sensations
Abstract
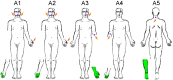
Previous work showed the existence of changes in the topographic organization within the somatosensory cortex (SI) in amputees with phantom limb pain, however, the link between nonpainful phantom sensations such as cramping or tingling or the percept of the limb and cortical changes is less clear. We used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in a highly selective group of limb amputees who experienced inducible and reproducible nonpainful phantom sensations. A standardized procedure was used to locate body sites eliciting phantom sensations in each amputee. Selected body sites that could systematically evoke phantom sensations were stimulated using electrical pulses in order to induce phasic phantom sensations. Homologous body parts were also stimulated in a group of matched controls. Activations related to evoked phantom sensations were found bilaterally in SI and the intraparietal sulci (IPS), which significantly correlated with the intensity of evoked phantom sensations. In addition, we found differences in intra- and interhemispheric interaction between amputees and controls during evoked phantom sensations. We assume that phantom sensations might be associated with a functional decoupling between bilateral SI and IPS, possibly resulting from transcallosal reorganization mechanisms following amputation.
Keywords: Evoked phantom sensations; Functional magnetic resonance imaging; Functional reorganization; Unilateral limb amputees.
Copyright © 2017. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures



References
-
- Benjamini Y., Hochberg Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society Series B. 1995;57:289–300.
-
- Björkman A., Weibull A., Olsrud J., Ehrsson H.H., Rosen B., Björkman-Burtscher I.M. Phantom digit somatotopy: A functional magnetic resonance imaging study in forearm amputees. The European Journal of Neuroscience. 2012;36(1):2098–2106. - PubMed
-
- Blanke O., Ortigue S., Landis T., Seeck M. Stimulating illusory own-body perceptions. Nature. 2002;419:269–270. - PubMed
-
- Bolognini N., Olgiati E., Maravita A., Ferraro F., Fregni F. Motor and parietal cortex stimulation for phantom limb pain and sensations. Pain. 2013;154(8):1274–1280. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

