JetValve: Rapid manufacturing of biohybrid scaffolds for biomimetic heart valve replacement
- PMID: 28445803
- PMCID: PMC5526340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2017.04.033
JetValve: Rapid manufacturing of biohybrid scaffolds for biomimetic heart valve replacement
Abstract
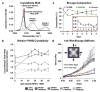
Tissue engineered scaffolds have emerged as a promising solution for heart valve replacement because of their potential for regeneration. However, traditional heart valve tissue engineering has relied on resource-intensive, cell-based manufacturing, which increases cost and hinders clinical translation. To overcome these limitations, in situ tissue engineering approaches aim to develop scaffold materials and manufacturing processes that elicit endogenous tissue remodeling and repair. Yet despite recent advances in synthetic materials manufacturing, there remains a lack of cell-free, automated approaches for rapidly producing biomimetic heart valve scaffolds. Here, we designed a jet spinning process for the rapid and automated fabrication of fibrous heart valve scaffolds. The composition, multiscale architecture, and mechanical properties of the scaffolds were tailored to mimic that of the native leaflet fibrosa and assembled into three dimensional, semilunar valve structures. We demonstrated controlled modulation of these scaffold parameters and show initial biocompatibility and functionality in vitro. Valves were minimally-invasively deployed via transapical access to the pulmonary valve position in an ovine model and shown to be functional for 15 h.
Keywords: Biohybrid; Heart valve; Nanofiber; Rapid manufacture; Rotary Jet Spinning; Tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures







Similar articles
-
Biodegradable and biomimetic elastomeric scaffolds for tissue-engineered heart valves.Acta Biomater. 2017 Jan 15;48:2-19. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2016.10.032. Epub 2016 Oct 22. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 27780764 Review.
-
Living nano-micro fibrous woven fabric/hydrogel composite scaffolds for heart valve engineering.Acta Biomater. 2017 Mar 15;51:89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2017.01.051. Epub 2017 Jan 18. Acta Biomater. 2017. PMID: 28110071
-
Fabrication of elastomeric scaffolds with curvilinear fibrous structures for heart valve leaflet engineering.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 Sep;103(9):3101-6. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35450. Epub 2015 Mar 27. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015. PMID: 25771748 Free PMC article.
-
Minimally-invasive implantation of living tissue engineered heart valves: a comprehensive approach from autologous vascular cells to stem cells.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010 Aug 3;56(6):510-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2010.04.024. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2010. PMID: 20670763
-
Fibrous scaffolds for building hearts and heart parts.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016 Jan 15;96:83-102. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.020. Epub 2015 Dec 4. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016. PMID: 26656602 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Strategies for Development of Synthetic Heart Valve Tissue Engineering Scaffolds.Prog Mater Sci. 2023 Oct;139:101173. doi: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2023.101173. Epub 2023 Jul 26. Prog Mater Sci. 2023. PMID: 37981978 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprinting Technology in Skin, Heart, Pancreas and Cartilage Tissues: Progress and Challenges in Clinical Practice.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Oct 14;18(20):10806. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182010806. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34682564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biofabrication of Sodium Alginate Hydrogel Scaffolds for Heart Valve Tissue Engineering.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8567. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158567. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955704 Free PMC article.
-
Human cell-derived tissue-engineered heart valve with integrated Valsalva sinuses: towards native-like transcatheter pulmonary valve replacements.NPJ Regen Med. 2019 Jun 17;4:14. doi: 10.1038/s41536-019-0077-4. eCollection 2019. NPJ Regen Med. 2019. PMID: 31240114 Free PMC article.
-
Materials and manufacturing perspectives in engineering heart valves: a review.Mater Today Bio. 2019 Dec 5;5:100038. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2019.100038. eCollection 2020 Jan. Mater Today Bio. 2019. PMID: 32211604 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chaikof EL. The development of prosthetic heart valves—lessons in form and function. New England Journal of Medicine. 2007;357(14):1368–1371. - PubMed
-
- Jana S, Tranquillo RT, Lerman A. Cells for tissue engineering of cardiac valves. Journal of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. 2015 - PubMed
-
- Robinson PS, Johnson SL, Evans MC, Barocas VH, Tranquillo RT. Functional tissue-engineered valves from cell-remodeled fibrin with commissural alignment of cell-produced collagen. Tissue Engineering Part A. 2008;14(1):83–95. - PubMed
-
- Jana S, Tefft B, Spoon D, Simari RD. Scaffolds for tissue engineering of cardiac valves. Acta biomaterialia. 2014;10(7):2877–2893. - PubMed
-
- Badylak SF. A scaffold immune microenvironment. Science. 2016;352(6283):298–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

