Methylation-mediated silencing of microRNA-211 promotes cell growth and epithelial to mesenchymal transition through activation of the AKT/β-catenin pathway in GBM
- PMID: 28445937
- PMCID: PMC5421919
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.15531
Methylation-mediated silencing of microRNA-211 promotes cell growth and epithelial to mesenchymal transition through activation of the AKT/β-catenin pathway in GBM
Abstract
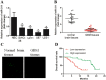
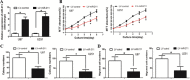
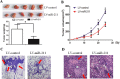
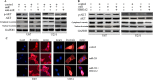
Aberrant expression of miR-211 has frequently been reported in cancer studies; however, its role in glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) has not been examined in detail. We investigated the function and the underlying mechanism of miR-211 in GBM. We revealed that miR-211 was downregulated in GBM tissues and cell lines. Restoration of miR-211 inhibited GBM cell growth and invasion both in vitro and in vivo. The epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) phenotype was reversed when miR-211 expression was restored. HMGA2 was identified as a down-stream target of miR-211. MiR-211 had an inhibitory effect on AKT/β-catenin signaling, which was reversed by HMGA2 overexpression or miR-211 restoration. In addition, miR-211 was transcriptionally repressed by EZH2-induced H3K27 trimethylation and promoter methylation. Overall, our findings revealed miR-211 as a tumor suppressor in GBM and mir-211 may be a potential therapeutic target for GBM patients.
Keywords: EZH2; HMGA2; epithelial to mesenchymal transition; glioblastoma; miR-211.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Reardon DA, Rich JN, Friedman HS, Bigner DD. Recent advances in the treatment of malignant astrocytoma. Journal of clinical oncology. 2006;24:1253–1265. - PubMed
-
- Wen PY, Kesari S. Malignant gliomas in adults. The New England journal of medicine. 2008;359:492–507. - PubMed
-
- Mrugala MM. Advances and challenges in the treatment of glioblastoma: a clinician’s perspective. Discovery medicine. 2013;15:221–230. - PubMed
-
- Plasterk RH. Micro RNAs in animal development. Cell. 2006;124:877–881. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

