The crosstalk between vascular MSCs and inflammatory mediators determines the pro-calcific remodelling of human atherosclerotic aneurysm
- PMID: 28446225
- PMCID: PMC5406974
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-017-0554-x
The crosstalk between vascular MSCs and inflammatory mediators determines the pro-calcific remodelling of human atherosclerotic aneurysm
Abstract
Background: Human mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) possess well-known reparative abilities, but any defect of the immunomodulatory activity and/or the differentiation process may determine the development of human diseases, including those affecting the vascular wall. MSCs residing within the human aortic wall represent a potential cell mediator of atherosclerotic aneurysm development.
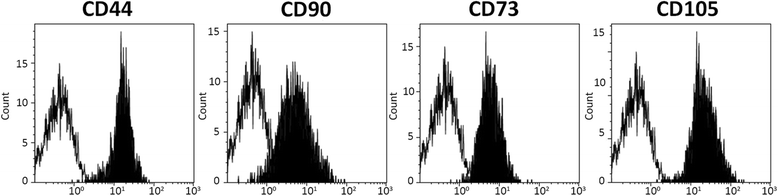
Methods: MSCs isolated from healthy and aneurysm aortas were characterized by flow cytometer and tested for differentiation properties. Healthy aorta (ha)-MSCs were then subjected to inflammatory stimuli to evaluate the microenvironmental impact on their function and involvement in vascular remodelling.
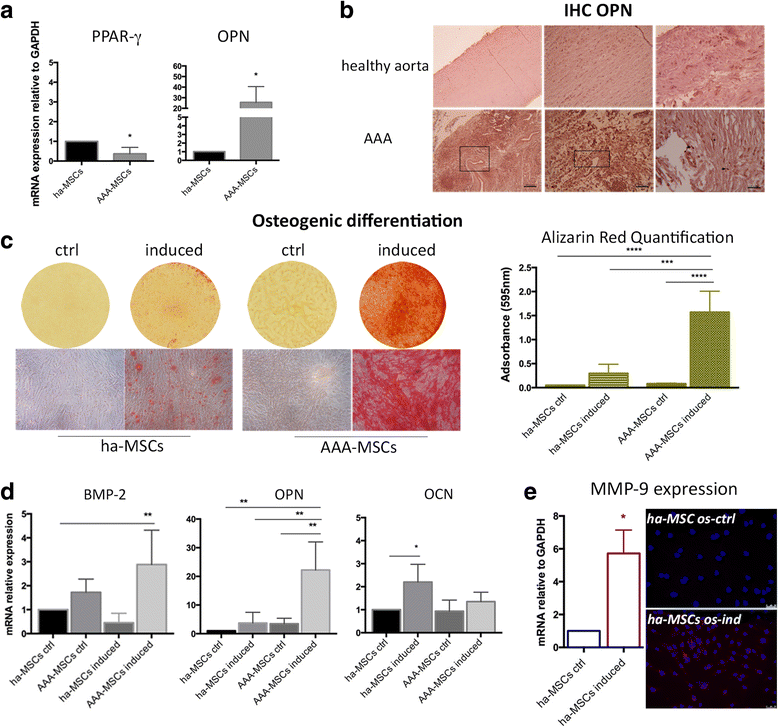
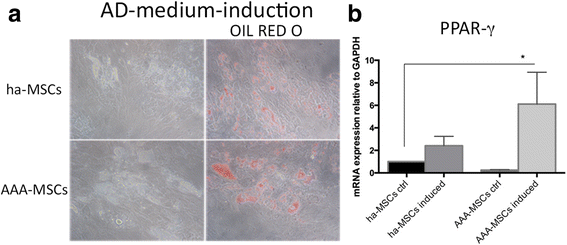
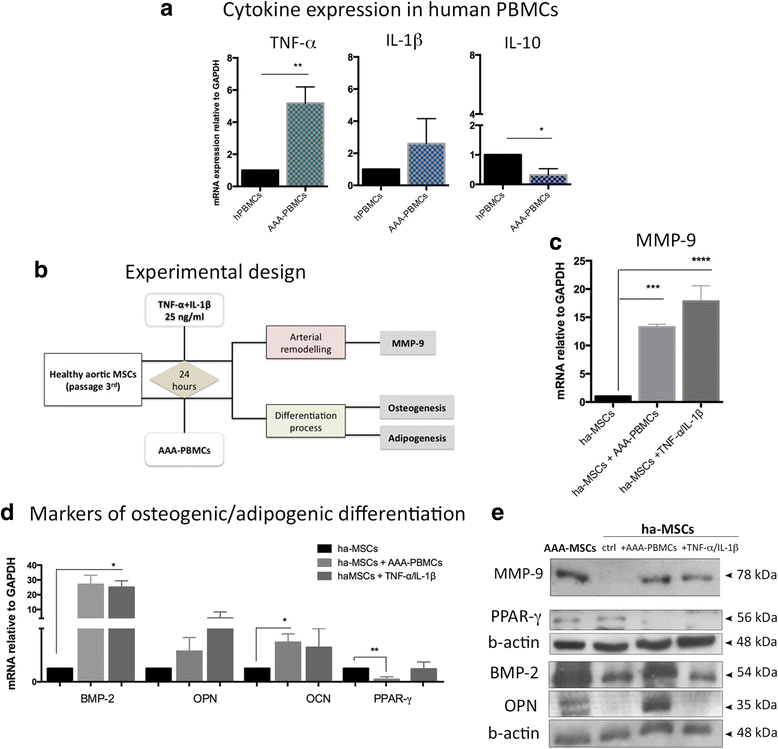
Results: Abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)-MSCs were isolated from calcified and inflamed aortas of 12 patients with high serum levels of MMP-9 protein. AAA-MSCs expressed typical mesenchymal markers and, in line with the histological analysis, elevated levels of OPN, an osteogenic marker also involved in vascular remodelling. AAA-MSCs were highly osteogenic and underwent intense calcium deposition under proper stimulation; moreover, AAA-MSCs were able to differentiate into tubule-like structures in Matrigel, even if the lack of CD146 and the reduced structural stability suggested an inefficient maturation process. We further demonstrated an association between osteogenesis and inflammation; indeed, ha-MSCs cultured with either cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β) or AAA-PBMCs showed increased expression of MMP-9 and osteogenic markers, to the detriment of the adipogenic regulator PPAR-γ. Interestingly, the culture with inflammatory cells highly stimulated ha-MSCs towards the osteogenic commitment.
Conclusions: AAA-MSCs displayed high osteogenic potential and pathological angiogenesis that represent crucial steps for AAA progression; we showed that the inflammatory process critically addresses human vascular MSCs towards a pathological behaviour, inducing vascular bone matrix deposition and remodelling. Inhibition of this pathway may represent a pharmacological approach against arterial calcification.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Atherosclerotic aneurysm; Calcification; Human aortic mesenchymal stem cells; Inflammation; Vascular remodelling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Human Vascular Wall Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Contribute to Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Pathogenesis Through an Impaired Immunomodulatory Activity and Increased Levels of Matrix Metalloproteinase-9.Circ J. 2015;79(7):1460-9. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-14-0857. Epub 2015 Apr 7. Circ J. 2015. PMID: 25854712
-
Proinflammatory Mediators Enhance the Osteogenesis of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells after Lineage Commitment.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0132781. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132781. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26176237 Free PMC article.
-
Different Drugs Effect on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Isolated From Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Ann Vasc Surg. 2020 Aug;67:490-496. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2020.03.001. Epub 2020 Mar 12. Ann Vasc Surg. 2020. PMID: 32173476
-
The Potential Role of Kallistatin in the Development of Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 Aug 11;17(8):1312. doi: 10.3390/ijms17081312. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27529213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoclastogenesis in Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms: A New Therapeutic Target.Curr Drug Targets. 2018;19(11):1233-1240. doi: 10.2174/1389450118666170925155044. Curr Drug Targets. 2018. PMID: 28950811 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological (or Synthetic) and Nutritional Agonists of PPAR-γ as Candidates for Cytokine Storm Modulation in COVID-19 Disease.Molecules. 2020 Apr 29;25(9):2076. doi: 10.3390/molecules25092076. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32365556 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Liver MSCs Retain Their Basic Cellular Properties in Chronically Inflamed Liver Tissue.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Dec 13;25(24):13374. doi: 10.3390/ijms252413374. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39769138 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal Stem/Progenitor Cells: The Prospect of Human Clinical Translation.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Aug 11;2020:8837654. doi: 10.1155/2020/8837654. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 33953753 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of klotho and stem cells in mediating vascular calcification (Review).Exp Ther Med. 2020 Dec;20(6):124. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.9252. Epub 2020 Sep 24. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 33005250 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Frequency, shape, and estimated volume of intracranial physiologic calcification in different age groups investigated by brain computed tomography scan: a retrospective study.Anat Cell Biol. 2022 Mar 31;55(1):63-71. doi: 10.5115/acb.21.137. Anat Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34866062 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

