The malaria testing and treatment landscape in Benin
- PMID: 28446236
- PMCID: PMC5405537
- DOI: 10.1186/s12936-017-1808-x
The malaria testing and treatment landscape in Benin
Abstract
Background: Since 2004, artemisinin-based combination therapy (ACT) has been the first-line treatment for uncomplicated malaria in Benin. In 2016, a medicine outlet survey was implemented to investigate the availability, price, and market share of anti-malarial treatment and malaria diagnostics. Results provide a timely and important benchmark to measure future interventions aimed at increasing access to quality malaria case management services.
Methods: Between July 5th to August 6th 2016, a cross sectional, nationally-representative malaria outlet survey was conducted in Benin. A census of all public and private outlets with potential to distribute malaria testing and/or treatment was implemented among 30 clusters (arrondissements). Outlets were eligible for inclusion in the study if they met at least one of three study criteria: (1) one or more anti-malarials reportedly in stock on the day of the survey; (2) one or more anti-malarials reportedly in stock within the 3 months preceding the survey; and/or (3) provided malaria blood testing. An audit was completed for all anti-malarials, malaria rapid diagnostic tests (RDT) and microscopy.
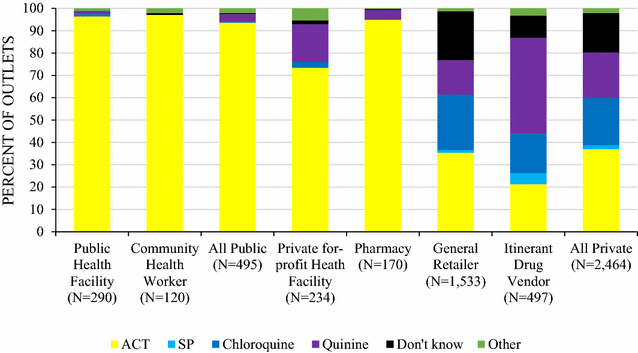
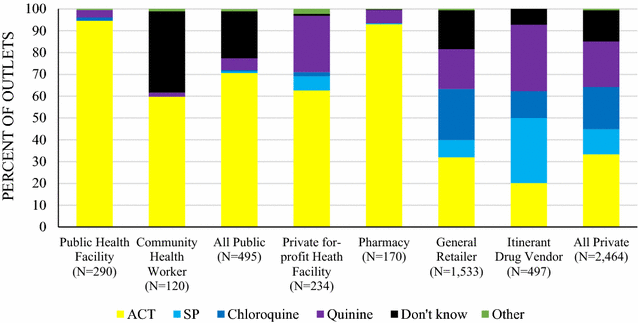
Results: 7260 outlets with the potential to sell or distribute anti-malarials were included in the census and 2966 were eligible and interviewed. A total of 17,669 anti-malarial and 494 RDT products were audited. Quality-assured ACT was available in 95.0% of all screened public health facilities and 59.4% of community health workers (CHW), and availability of malaria blood testing was 94.7 and 68.4% respectively. Sulfadoxine-pyrimethamine (SP) was available in 73.9% of public health facilities and not found among CHWs. Among private-sector outlets stocking at least one anti-malarial, non-artemisinin therapies were most commonly available (94.0% of outlets) as compared to quality-assured ACT (36.1%). 31.3% of the ACTs were marked with a "green leaf" logo, suggesting leakage of a co-paid ACT into Benin's unsubsidized ACT market from another country. 78.5% of the anti-malarials distributed were through the private sector, typically through general retailers (47.6% of all anti-malarial distribution). ACT comprised 44% of the private anti-malarial market share. Private-sector price of quality-assured ACT ($1.35) was three times more expensive than SP ($0.42) or chloroquine ($0.41). Non-artemisinin therapies were cited as the most effective treatment for uncomplicated malaria among general retailers and itinerant drug vendors.
Conclusions: The ACTwatch data has shown the importance of the private sector in terms of access to malaria treatment for the majority of the population in Benin. These findings highlight the need for increased engagement with the private sector to improve malaria case management and an immediate need for a national ACT subsidy.
Keywords: ACT subsidy; Artemisinin-based combination therapy; Benin; Diagnostic test; Malaria case management; Private sector; Public sector.
Figures
References
-
- WHO. World malaria report. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016. World Health Organization website http://www.who.int/malaria/publications/world-malaria-report-2016/report.... Accessed 3 Apr 2017.
-
- Yaya S, Ze A. Le fardeau socio-économique du paludisme: Une analyse économétrique. Quebec City: Presses de l’Université Laval; 2013.
-
- ACTwatch Group. ACTwatch baseline and endline household survey results 2009–2012: Benin, Democratic Republic of Congo, Madagascar, Nigeria, Uganda, Zambia. Washington, DC. 2013. ACTwatch website. http://www.actwatch.info/sites/default/files/content/publications/attach.... Accessed 3 Apr 2017.
-
- ICF Macro. Enquête Démographique et de Santé du Bénin 2011–2012. Calverton, Maryland, USA. 2013. Demographic and Health Survey website. http://dhsprogram.com/publications/publication-FR270-DHS-Final-Reports.cfm. Accessed Apr 4 2017.
-
- World Bank. Les efforts du Bénin pour la réduction de la pauvreté (The efforts of Benin to reduce poverty). Cotonou, Benin. 2014. International Monetary Fund website. https://www.imf.org/external/french/pubs/ft/scr/2011/cr11307f.pdf.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous