Temporal integration and 1/ f power scaling in a circuit model of cerebellar interneurons
- PMID: 28446587
- PMCID: PMC5506264
- DOI: 10.1152/jn.00789.2016
Temporal integration and 1/ f power scaling in a circuit model of cerebellar interneurons
Abstract
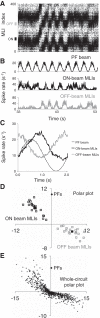
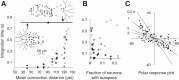
Inhibitory interneurons interconnected via electrical and chemical (GABAA receptor) synapses form extensive circuits in several brain regions. They are thought to be involved in timing and synchronization through fast feedforward control of principal neurons. Theoretical studies have shown, however, that whereas self-inhibition does indeed reduce response duration, lateral inhibition, in contrast, may generate slow response components through a process of gradual disinhibition. Here we simulated a circuit of interneurons (stellate and basket cells) of the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex and observed circuit time constants that could rise, depending on parameter values, to >1 s. The integration time scaled both with the strength of inhibition, vanishing completely when inhibition was blocked, and with the average connection distance, which determined the balance between lateral and self-inhibition. Electrical synapses could further enhance the integration time by limiting heterogeneity among the interneurons and by introducing a slow capacitive current. The model can explain several observations, such as the slow time course of OFF-beam inhibition, the phase lag of interneurons during vestibular rotation, or the phase lead of Purkinje cells. Interestingly, the interneuron spike trains displayed power that scaled approximately as 1/f at low frequencies. In conclusion, stellate and basket cells in cerebellar cortex, and interneuron circuits in general, may not only provide fast inhibition to principal cells but also act as temporal integrators that build a very short-term memory.NEW & NOTEWORTHY The most common function attributed to inhibitory interneurons is feedforward control of principal neurons. In many brain regions, however, the interneurons are densely interconnected via both chemical and electrical synapses but the function of this coupling is largely unknown. Based on large-scale simulations of an interneuron circuit of cerebellar cortex, we propose that this coupling enhances the integration time constant, and hence the memory trace, of the circuit.
Keywords: basket cell; cerebellum; computational model; integrator; lateral inhibition; stellate cell.
Copyright © 2017 the American Physiological Society.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Reliable control of spike rate and spike timing by rapid input transients in cerebellar stellate cells.Neuroscience. 2004;124(2):305-17. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2003.11.015. Neuroscience. 2004. PMID: 14980381
-
Synaptic integration in a model of cerebellar granule cells.J Neurophysiol. 1994 Aug;72(2):999-1009. doi: 10.1152/jn.1994.72.2.999. J Neurophysiol. 1994. PMID: 7527078
-
Synaptic shunting by a baseline of synaptic conductances modulates responses to inhibitory input volleys in cerebellar Purkinje cells.Cerebellum. 2004;3(2):112-25. doi: 10.1080/14734220410031990. Cerebellum. 2004. PMID: 15233579
-
Electrical synapses between GABA-releasing interneurons.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001 Jun;2(6):425-33. doi: 10.1038/35077566. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2001. PMID: 11389476 Review.
-
Molecular layer interneurons of the cerebellum: developmental and morphological aspects.Cerebellum. 2015 Oct;14(5):534-56. doi: 10.1007/s12311-015-0648-x. Cerebellum. 2015. PMID: 25599913 Review.
Cited by
-
Neural correlates of integration processes during dynamic face perception.Sci Rep. 2022 Jan 7;12(1):118. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02808-9. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 34996892 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Principles of Supervised Learning in the Cerebellum.Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018 Jul 8;41:233-253. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-080317-061948. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29986160 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diverse Neuron Properties and Complex Network Dynamics in the Cerebellar Cortical Inhibitory Circuit.Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 Nov 7;12:267. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2019.00267. eCollection 2019. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31787879 Free PMC article.
-
Cerebellar Coordination of Neuronal Communication in Cerebral Cortex.Front Syst Neurosci. 2022 Jan 11;15:781527. doi: 10.3389/fnsys.2021.781527. eCollection 2021. Front Syst Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35087384 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-type-specific firing patterns in a V1 cortical column model depend on feedforward and feedback-driven states.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Apr 23;21(4):e1012036. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012036. eCollection 2025 Apr. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40267074 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Andersen P, Eccles JC, Voorhoeve PE. Postsynaptic inhibition of cerebellar Purkinje cells. J Neurophysiol 27: 1138–1153, 1964. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

