Expandable Mg-based Helical Stent Assessment using Static, Dynamic, and Porcine Ex Vivo Models
- PMID: 28446750
- PMCID: PMC5430820
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01214-4
Expandable Mg-based Helical Stent Assessment using Static, Dynamic, and Porcine Ex Vivo Models
Abstract
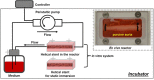
A bioresorbable metallic helical stent was explored as a new device opportunity (magnesium scaffold), which can be absorbed by the body without leaving a trace and simultaneously allowing restoration of vasoreactivity with the potential for vessel remodeling. In this study, developed Mg-based helical stent was inserted and expanded in vessels with subsequent degradation in various environments including static, dynamic, and porcine ex vivo models. By assessing stent degradation in three different environments, we observed: (1) stress- and flow-induced degradation; (2) a high degradation rate in the dynamic reactor; (3) production of intermediate products (MgO/Mg(OH)2 and Ca/P) during degradation; and (4) intermediate micro-gas pocket formation in the neighboring tissue ex vivo model. Overall, the expandable Mg-based helical stent employed as a scaffold performed well, with expansion rate (>100%) in porcine ex vivo model.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- Kaul, S. Advisory Board. http://www.advisory.com/daily-briefing/2013/10/30/cardiologists-will-sto... (2013).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

