Variants in the IL7RA gene confer susceptibility to multiple sclerosis in Caucasians: evidence based on 9734 cases and 10436 controls
- PMID: 28446795
- PMCID: PMC5430888
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-01345-8
Variants in the IL7RA gene confer susceptibility to multiple sclerosis in Caucasians: evidence based on 9734 cases and 10436 controls
Abstract
Recently, numerous genome wide association studies (GWAS) and other case-control association studies examining the relationship between interleukin-7 receptor α chain (IL7RA) gene rs3194051, rs987107, rs11567686, and rs11567685 variants and multiple sclerosis (MS) risk have been conducted, but the conclusions have been inconsistent. The main objective of this meta-analysis was to more precisely explore the association of these four IL7RA variants with MS development. Twenty-seven eligible studies involving 9734 cases and 10436 controls were included in the present meta-analysis. Power calculation, publication bias, sensitivity analysis and cumulative meta-analysis were performed to derive a reliable conclusion. Our study indicated three IL7RA loci were significantly associated with increasing MS risk (rs3194051: recessive model: OR = 1.22, 95% CI 1.08-1.38; rs987107: recessive model: OR = 1.44, 95% CI 1.22-1.69; and rs11567686: dominant model: OR = 1.18, 95% CI 1.01-1.37). Additionally, IL7RA rs11567685 variants might not be related to MS development. In all, IL7RA locus polymorphisms could play an important role in the predisposition to MS, which could contribute to a better understanding the pathogenesis of multiple sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
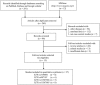



References
-
- Tullman MJ. Overview of the epidemiology, diagnosis, and disease progression associated with multiple sclerosis. Am J Manag Care. 2013;19:S15–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

