Thromboelastographic changes during laparoscopic fundoplication
- PMID: 28446928
- PMCID: PMC5397544
- DOI: 10.5114/wiitm.2017.66474
Thromboelastographic changes during laparoscopic fundoplication
Abstract
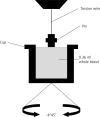
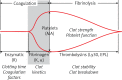
Introduction: Thromboelastography (TEG) is a technique that measures coagulation processes and surveys the properties of a viscoelastic blood clot, from its formation to lysis.
Aim: To determine the possible hypercoagulability state and the effect of antithrombotic prophylaxis on thromboelastogram results and development of venous thrombosis during laparoscopic fundoplication.
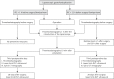
Material and methods: The study was performed on 106 patients who were randomized into two groups. The first group received low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) 12 h before the operation, and 6 and 30 h after it. The second group received LMWH only 1 h before the laparoscopic fundoplication. The TEG profile was collected before LMWH injection, 1 h after the introduction of the laparoscope and 15 min after the surgery was completed.
Results: There was no significant difference in thromboelastography R-time between the groups before low-molecular-weight heparin injection. In group I preoperative R-values significantly decreased 1 h after the introduction of the laparoscope, after the end of surgery and on the third postoperative day. K-time values decreased significantly on the third postoperative day compared with the results before low-molecular-weight heparin injection, and after the operation. In group II, preoperative R-values significantly decreased 1 h after the introduction of the laparoscope, and after surgery. K-time values did not change significantly during or after the laparoscopic operation.
Conclusions: Our study results demonstrated that the hypercoagulation state (according to the TEG results) was observed during and after laparoscopic fundoplication in patients when LMWH was administered 12 h before the operation together with intraoperative intermittent pneumatic compression. The optimal anticoagulation was obtained when LMWH was administered 1 h before fundoplication.
Keywords: hypercoagulability; laparoscopic fundoplication; thromboelastogram.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kiudelis M, Gerbutavičius R, Gerbutavičienė R, et al. A combination effect of low-molecular-weight heparin and intermittent pneumatic compression device for thrombosis prevention during laparoscopic fundoplication. Medicina (Kaunas) 2010;46:18–23. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen NT, Owings JT, Gosselin R, et al. Systemic coagulation and fibrinolysis after laparoscopic and open gastrib bypass. Arch Surg. 2001;136:909–16. - PubMed
-
- Lee BY, Butler G, Al-Waili N, et al. Role of thrombelastograph haemostasis analyser in detection hypercoagulability following surgery with and without use of intermittent pneumatic compression. J Med Eng Technol. 2010;34:166–71. - PubMed
-
- Sato H, Izuta S, Misumi T, et al. Incidence and clinical characteristics of perioperative pulmonary thromboembolism under the use of intermittent pneumatic compression as preventive measure. Masui. 2003;52:1300–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
