Endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early stage esophageal cancer
- PMID: 28446997
- PMCID: PMC5387148
- DOI: 10.21037/acs.2017.03.15
Endoscopic submucosal dissection and endoscopic mucosal resection for early stage esophageal cancer
Abstract
Mortality from esophageal cancer remains high despite advances in medical therapy. Although the incidence of squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus remains unchanged, the incidence of the esophageal adenocarcinoma has increased over time. Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD and obesity are contributing factors to the development of Barrett's esophagus and subsequent development of adenocarcinoma. Early recognition of the disease can lead to resection of esophageal cancer prior to the development of lymphovascular invasion. Various modalities have been implemented to aid identification of precancerous lesions and early esophageal cancer. Chromoendoscopy, narrowband imaging and endoscopic ultrasound examination are typically used for evaluating early esophageal lesions. Recently, confocal laser endomicroscopy (CLE) and volumetric laser scanning were implemented with promising results. Endoscopic management of early esophageal cancer may be done using endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD). Both techniques allow resection of the mucosa (and possibly a portion of the submucosa) containing the early tumor without interruption of deeper layers. A submucosal injection creating a cushion coupled with snare resection or cap assisted mucosal suction followed by ligation and snare resection are the most common techniques of EMR. EMR can remove lesions less than 2 cm in size en bloc. Larger lesions may require resection in piecemeal fashion. This may limit assessment of the margins of the lesion and orienting the lesion's border. ESD offers en bloc dissection of the lesion regardless of its size. ESD is performed with specialized needle knives, which allow incision followed by careful dissection of the lesion within the submucosal layer. Tumor recurrence after ESD is rare but the technique is labor intensive and has an increased risk of perforation. Esophageal stenosis remains a concern after extensive EMR or ESD. Dilation with balloon or stent placement is usually sufficient to treat post-resection stenosis.
Keywords: Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD); early esophageal cancer; endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


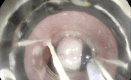

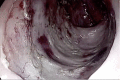

References
-
- Zargar SA, Khuroo MS, Jan GM, et al. Prospective comparison of the value of brushings before and after biopsy in the endoscopic diagnosis of gastroesophageal malignancy. Acta Cytol 1991;35:549-52. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
