Prediction of Breast and Prostate Cancer Risks in Male BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers Using Polygenic Risk Scores
- PMID: 28448241
- PMCID: PMC5501359
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2016.69.4935
Prediction of Breast and Prostate Cancer Risks in Male BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers Using Polygenic Risk Scores
Abstract
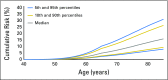
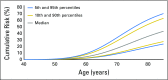
Purpose BRCA1/2 mutations increase the risk of breast and prostate cancer in men. Common genetic variants modify cancer risks for female carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations. We investigated-for the first time to our knowledge-associations of common genetic variants with breast and prostate cancer risks for male carriers of BRCA1/ 2 mutations and implications for cancer risk prediction. Materials and Methods We genotyped 1,802 male carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations from the Consortium of Investigators of Modifiers of BRCA1/2 by using the custom Illumina OncoArray. We investigated the combined effects of established breast and prostate cancer susceptibility variants on cancer risks for male carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations by constructing weighted polygenic risk scores (PRSs) using published effect estimates as weights. Results In male carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations, PRS that was based on 88 female breast cancer susceptibility variants was associated with breast cancer risk (odds ratio per standard deviation of PRS, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.19 to 1.56; P = 8.6 × 10-6). Similarly, PRS that was based on 103 prostate cancer susceptibility variants was associated with prostate cancer risk (odds ratio per SD of PRS, 1.56; 95% CI, 1.35 to 1.81; P = 3.2 × 10-9). Large differences in absolute cancer risks were observed at the extremes of the PRS distribution. For example, prostate cancer risk by age 80 years at the 5th and 95th percentiles of the PRS varies from 7% to 26% for carriers of BRCA1 mutations and from 19% to 61% for carriers of BRCA2 mutations, respectively. Conclusion PRSs may provide informative cancer risk stratification for male carriers of BRCA1/2 mutations that might enable these men and their physicians to make informed decisions on the type and timing of breast and prostate cancer risk management.
Figures

Comment in
-
Fine Tuning the Risk of Hereditary Cancer Using Genome-Wide Association Studies.J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jul 10;35(20):2224-2225. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2017.72.8071. Epub 2017 May 8. J Clin Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28481708 No abstract available.
References
-
- Rizzolo P, Silvestri V, Tommasi S, et al. Male breast cancer: Genetics, epigenetics, and ethical aspects. Ann Oncol. 2013;24(suppl 8):viii75–viii82. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- RP-PG-0707-10031/DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 11174/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 20861/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- U01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 12677/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R01 CA116167/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 15007/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA016058/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148065/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 23382/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 203477/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA140323/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA176785/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 17528/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- RC4 CA153828/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA142996/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA125183/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 CA164920/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA168524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA161032/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA128978/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP011019/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N02 CP065504/CP/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA116201/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA113916/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 17523/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

