A genome-wide analysis of the RNA-guided silencing pathway in coffee reveals insights into its regulatory mechanisms
- PMID: 28448529
- PMCID: PMC5407642
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0176333
A genome-wide analysis of the RNA-guided silencing pathway in coffee reveals insights into its regulatory mechanisms
Abstract
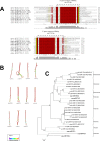
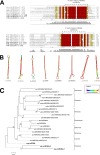
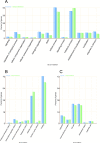
microRNAs (miRNAs) are derived from self-complementary hairpin structures, while small-interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are derived from double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) or hairpin precursors. The core mechanism of sRNA production involves DICER-like (DCL) in processing the smallRNAs (sRNAs) and ARGONAUTE (AGO) as effectors of silencing, and siRNA biogenesis also involves action of RNA-Dependent RNA Polymerase (RDR), Pol IV and Pol V in biogenesis. Several other proteins interact with the core proteins to guide sRNA biogenesis, action, and turnover. We aimed to unravel the components and functions of the RNA-guided silencing pathway in a non-model plant species of worldwide economic relevance. The sRNA-guided silencing complex members have been identified in the Coffea canephora genome, and they have been characterized at the structural, functional, and evolutionary levels by computational analyses. Eleven AGO proteins, nine DCL proteins (which include a DCL1-like protein that was not previously annotated), and eight RDR proteins were identified. Another 48 proteins implicated in smallRNA (sRNA) pathways were also identified. Furthermore, we identified 235 miRNA precursors and 317 mature miRNAs from 113 MIR families, and we characterized ccp-MIR156, ccp-MIR172, and ccp-MIR390. Target prediction and gene ontology analyses of 2239 putative targets showed that significant pathways in coffee are targeted by miRNAs. We provide evidence of the expansion of the loci related to sRNA pathways, insights into the activities of these proteins by domain and catalytic site analyses, and gene expression analysis. The number of MIR loci and their targeted pathways highlight the importance of miRNAs in coffee. We identified several roles of sRNAs in C. canephora, which offers substantial insight into better understanding the transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of this major crop.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Brodersen P, Voinnet O. The diversity of RNA silencing pathways in plants. Trends in Genetics. 2006;22(5):268–80. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2006.03.003 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Axtell MJ. Classification and comparison of small RNAs from plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2013;64(1):137–59. - PubMed
-
- Borges F, Martienssen RA. The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2015;16(12):727–41. Epub 2015/11/05. PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc4948178. doi: 10.1038/nrm4085 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kim YJ, Zheng B, Yu Y, Won SY, Mo B, Chen X. The role of Mediator in small and long noncoding RNA production in Arabidopsis thaliana. The EMBO journal. 2011;30(5):814–22. Epub 2011/01/22. PubMed Central PMCID: PMCPmc3049218. doi: 10.1038/emboj.2011.3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

