Toxin-antitoxin systems and their role in disseminating and maintaining antimicrobial resistance
- PMID: 28449040
- PMCID: PMC5812544
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fux006
Toxin-antitoxin systems and their role in disseminating and maintaining antimicrobial resistance
Abstract
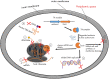
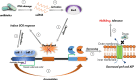
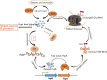
Toxin-antitoxin systems (TAs) are ubiquitous among bacteria and play a crucial role in the dissemination and evolution of antibiotic resistance, such as maintaining multi-resistant plasmids and inducing persistence formation. Generally, activities of the toxins are neutralised by their conjugate antitoxins. In contrast, antitoxins are more liable to degrade under specific conditions such as stress, and free active toxins interfere with essential cellular processes including replication, translation and cell-wall synthesis. TAs have also been shown to be responsible for plasmid maintenance, stress management, bacterial persistence and biofilm formation. We discuss here the recent findings of these multifaceted TAs (type I-VI) and in particular examine the role of TAs in augmenting the dissemination and maintenance of multi-drug resistance in bacteria.
Keywords: addictive systems; antimicrobial resistance; persistence; toxin–antitoxins.
© FEMS 2017. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Amato SM, Orman MA, Brynildsen MP. Metabolic control of persister formation in Escherichia coli. Mol Cell 2013;50:475–87. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

