Neuro-symbolic representation learning on biological knowledge graphs
- PMID: 28449114
- PMCID: PMC5860058
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btx275
Neuro-symbolic representation learning on biological knowledge graphs
Abstract
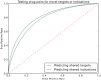
Motivation: Biological data and knowledge bases increasingly rely on Semantic Web technologies and the use of knowledge graphs for data integration, retrieval and federated queries. In the past years, feature learning methods that are applicable to graph-structured data are becoming available, but have not yet widely been applied and evaluated on structured biological knowledge. Results: We develop a novel method for feature learning on biological knowledge graphs. Our method combines symbolic methods, in particular knowledge representation using symbolic logic and automated reasoning, with neural networks to generate embeddings of nodes that encode for related information within knowledge graphs. Through the use of symbolic logic, these embeddings contain both explicit and implicit information. We apply these embeddings to the prediction of edges in the knowledge graph representing problems of function prediction, finding candidate genes of diseases, protein-protein interactions, or drug target relations, and demonstrate performance that matches and sometimes outperforms traditional approaches based on manually crafted features. Our method can be applied to any biological knowledge graph, and will thereby open up the increasing amount of Semantic Web based knowledge bases in biology to use in machine learning and data analytics.
Availability and implementation: https://github.com/bio-ontology-research-group/walking-rdf-and-owl.
Contact: robert.hoehndorf@kaust.edu.sa.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
References
-
- Baader F. et al. (2003) The Description Logic Handbook: Theory, Implementation and Applications. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
-
- Belhajjame K. et al. (2012). PROV-O: The PROV ontology. Technical report, W3C.
-
- Belleau F. et al. (2008) Bio2RDF: Towards a mashup to build bioinformatics knowledge systems. J. Biomed. Inf., 41, 706–716. - PubMed
-
- Berners-Lee T. et al. (2001) The Semantic Web. Sci. Am., 284, 28–37.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

