Protective effect of propofol preconditioning on ischemia-reperfusion injury in human hepatocyte
- PMID: 28449478
- PMCID: PMC5394059
- DOI: 10.21037/jtd.2017.02.80
Protective effect of propofol preconditioning on ischemia-reperfusion injury in human hepatocyte
Abstract
Background: Blood reperfusion after ischemia is the main measure to restore cell function. This study was aimed to explore the effect of propofol on rat and cell models of liver ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury, and to investigate its possible mechanism.
Methods: Wistar rats were divided into four groups: control group, sham group, I/R group, and propofol group. Human hepatocyte HL7702 was divided into six groups: control group, I/R group and propofol (5, 10, 20 and 40 µmol/L) groups. After the animal and cell models were established, the alanine aminotransferase (ALT), aspartate aminotransferase (AST), malondialdehyde (MDA) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) levels in liver tissues and hepatocytes were measured. Cell viability and apoptosis of hepatocytes were respectively determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide assay and flow cytometry. Furthermore, the expressions of apoptosis-related proteins in hepatocytes were determined by Western blot analysis.
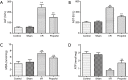
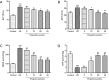
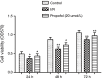
Results: ALT, AST and MDA levels were all decreased significantly, and the ATP level was increased significantly in propofol group compared with that in I/R group in both liver tissues and hepatocytes. Additionally, cell viability of hepatocytes in propofol group was higher than that in I/R group, while the percentage of apoptotic cells in propofol group was less than that in I/R group. Moreover, the expression of caspase-3 decreased and the expression of Bcl-2 increased significantly after propofol preconditioning.
Conclusions: Our findings suggested that propofol preconditioning might be an effective strategy for protecting the liver from I/R injury, which might provide a scientific basis for clinical application.
Keywords: Propofol; apoptosis; cell viability; hepatocyte; liver ischemia-reperfusion injury (liver I/R injury).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of propofol on cardiomyocytes apoptosis and its mechanism after ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat hearts].Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2008 Feb;24(1):56-61. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi. 2008. PMID: 21141559 Chinese.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning protects liver ischemia-reperfusion injury by regulating eNOS-NO pathway and liver microRNA expressions in fatty liver rats.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017 Aug 15;16(4):387-394. doi: 10.1016/S1499-3872(17)60006-7. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2017. PMID: 28823369
-
Ischemic preconditioning attenuates morphological and biochemical changes in hepatic ischemia/reperfusion in rats.Pathobiology. 2010;77(3):136-46. doi: 10.1159/000292647. Epub 2010 May 28. Pathobiology. 2010. PMID: 20516729
-
Ischemic preconditioning enhances hepatocyte proliferation in the early phase after ischemia under hemi-hepatectomy in rats.Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012 Oct;11(5):521-6. doi: 10.1016/s1499-3872(12)60217-3. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2012. PMID: 23060398
-
A meta-analysis and systematic review of propofol on liver ischemia-reperfusion injury protection during hepatocellular carcinoma anesthesia surgery.Ann Palliat Med. 2021 Jun;10(6):6726-6735. doi: 10.21037/apm-21-1242. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Ann Palliat Med. 2021. PMID: 34154355
Cited by
-
Inhaled Argon Impedes Hepatic Regeneration after Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 30;21(15):5457. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155457. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751707 Free PMC article.
-
Sevoflurane exerts improved protective effects than propofol on hypoxia-reoxygenation injury by regulating the microRNA-221-5p/ADAM8 axis in cardiomyocytes.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Aug;22(2):893. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10325. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34257708 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of remifentanil and propofol on distant organ lung injury in an ischemia-reperfusion model.Open Med (Wars). 2021 Nov 8;16(1):1673-1680. doi: 10.1515/med-2021-0381. eCollection 2021. Open Med (Wars). 2021. PMID: 34761118 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol-induced MiR-20b expression initiates endogenous cellular signal changes mitigating hypoxia/re-oxygenation-induced endothelial autophagy in vitro.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 13;11(8):681. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02828-9. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32826852 Free PMC article.
-
Propofol protects human cardiac cells against chemical hypoxiainduced injury by regulating the JNK signaling pathways.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1864-1870. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8440. Epub 2020 Jan 8. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32104242 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
