Differential regulation of surface receptor expression, proliferation, and apoptosis in HaCaT cells stimulated with interferon-γ, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor-α, or muramyl dipeptide
- PMID: 28449603
- PMCID: PMC5806789
- DOI: 10.1177/0394632017707611
Differential regulation of surface receptor expression, proliferation, and apoptosis in HaCaT cells stimulated with interferon-γ, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor-α, or muramyl dipeptide
Abstract
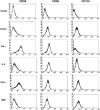
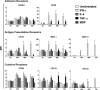
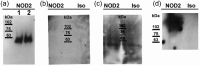
Keratinocytes are routinely subjected to both internal and external stimulation. This study investigates the effects of interferon gamma, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and the synthetic immunomodulator muramyl dipeptide on the human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT. Following HaCaT stimulation with cytokines or muramyl dipeptide for different time periods, changes in the expression of different cell surface receptors, cell proliferation, and cell apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry, tritiated thymidine uptake, and annexin-V staining, respectively. A significant decrease in the expression of CD49d was found upon treatment with interleukin-4. Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha increased the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and major histocompatibility complex class I, whereas major histocompatibility complex class II and CD1b were only upregulated by interferon gamma. Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha had opposite effects regarding CD119 expression, with the former downregulating, while the latter upregulating its expression. Of the stimuli tested, only interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha significantly inhibited proliferation of HaCaT cells, yet only interferon gamma played a significant role in inducing HaCaT cell apoptosis. Our data demonstrate differential effects of the three tested cytokines on keratinocytes and reveal that the absence of HaCaT cell responses to muramyl dipeptide is associated with undetectable levels of its cytoplasmic receptor, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2.
Keywords: CD molecules; apoptosis; cytokines; keratinocytes; muramyl dipeptide; surface receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
Interferon gamma boosts the nucleotide oligomerization domain 2-mediated signaling pathway in human dendritic cells in an X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and mammalian target of rapamycin-dependent manner.Cell Mol Immunol. 2017 Apr;14(4):380-391. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.90. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Cell Mol Immunol. 2017. PMID: 26521691 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon (IFN)-gamma is a main mediator of keratinocyte (HaCaT) apoptosis and contributes to autocrine IFN-gamma and tumour necrosis factor-alpha production.Br J Dermatol. 2005 Jun;152(6):1134-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.06508.x. Br J Dermatol. 2005. PMID: 15948973
-
Z-100, extracted from Mycobacterium tuberculosis strain Aoyama B, promotes TNF-α production via nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain containing 2 (Nod2)-dependent NF-κB activation in RAW264.7 cells.Mol Immunol. 2015 Mar;64(1):218-27. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2014.11.017. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Mol Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25499802
-
Icariin inhibits TNF-α/IFN-γ induced inflammatory response via inhibition of the substance P and p38-MAPK signaling pathway in human keratinocytes.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Dec;29(2):401-407. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.023. Epub 2015 Oct 24. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26507164
-
Biology and therapy with biologic agents in gynecologic cancer.Curr Opin Oncol. 1992 Oct;4(5):946-54. doi: 10.1097/00001622-199210000-00020. Curr Opin Oncol. 1992. PMID: 1457511 Review.
Cited by
-
Signature identification based on immunogenic cell death-related lncRNAs to predict the prognosis and immune activity of patients with endometrial carcinoma.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 30;13(6):2913-2937. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2243. Epub 2024 Jun 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38988945 Free PMC article.
-
The Modulatory Influence of Plant-Derived Compounds on Human Keratinocyte Function.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 19;22(22):12488. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212488. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ribes nigrum Leaf Extract Preferentially Inhibits IFN-γ-Mediated Inflammation in HaCaT Keratinocytes.Molecules. 2021 May 20;26(10):3044. doi: 10.3390/molecules26103044. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34065200 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Biotinylated PAMAM G3 Dendrimers Conjugated with COX-2 Inhibitor (celecoxib) and PPARγ Agonist (Fmoc-L-Leucine) on Human Normal Fibroblasts, Immortalized Keratinocytes and Glioma Cells in Vitro.Molecules. 2019 Oct 22;24(20):3801. doi: 10.3390/molecules24203801. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31652556 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial activity of NK cells to Trypanosoma cruzi infected human primary Keratinocytes.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024 Jul 22;18(7):e0012255. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0012255. eCollection 2024 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2024. PMID: 39038032 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Freedberg IM, Tomic-Canic M, Komine M, et al. (2001) Keratins and the keratinocyte activation cycle. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 116: 633–640. - PubMed
-
- Uchi H, Terao H, Koga T, et al. (2000) Cytokines and chemokines in the epidermis. Journal of Dermatological Science 24(Suppl. 1): S29–S38. - PubMed
-
- Caughman SW, Li LJ, Degitz K. (1990) Characterization and functional analysis of interferon-gamma-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in human keratinocytes and A-431 cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 94: 22S–26S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

