Differential regulation of surface receptor expression, proliferation, and apoptosis in HaCaT cells stimulated with interferon-γ, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor-α, or muramyl dipeptide
- PMID: 28449603
- PMCID: PMC5806789
- DOI: 10.1177/0394632017707611
Differential regulation of surface receptor expression, proliferation, and apoptosis in HaCaT cells stimulated with interferon-γ, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor-α, or muramyl dipeptide
Abstract
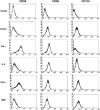
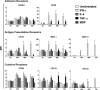
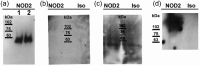
Keratinocytes are routinely subjected to both internal and external stimulation. This study investigates the effects of interferon gamma, interleukin-4, tumor necrosis factor alpha, and the synthetic immunomodulator muramyl dipeptide on the human keratinocyte cell line, HaCaT. Following HaCaT stimulation with cytokines or muramyl dipeptide for different time periods, changes in the expression of different cell surface receptors, cell proliferation, and cell apoptosis were evaluated by flow cytometry, tritiated thymidine uptake, and annexin-V staining, respectively. A significant decrease in the expression of CD49d was found upon treatment with interleukin-4. Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha increased the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 and major histocompatibility complex class I, whereas major histocompatibility complex class II and CD1b were only upregulated by interferon gamma. Interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha had opposite effects regarding CD119 expression, with the former downregulating, while the latter upregulating its expression. Of the stimuli tested, only interferon gamma and tumor necrosis factor alpha significantly inhibited proliferation of HaCaT cells, yet only interferon gamma played a significant role in inducing HaCaT cell apoptosis. Our data demonstrate differential effects of the three tested cytokines on keratinocytes and reveal that the absence of HaCaT cell responses to muramyl dipeptide is associated with undetectable levels of its cytoplasmic receptor, nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-containing protein 2.
Keywords: CD molecules; apoptosis; cytokines; keratinocytes; muramyl dipeptide; surface receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Freedberg IM, Tomic-Canic M, Komine M, et al. (2001) Keratins and the keratinocyte activation cycle. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 116: 633–640. - PubMed
-
- Uchi H, Terao H, Koga T, et al. (2000) Cytokines and chemokines in the epidermis. Journal of Dermatological Science 24(Suppl. 1): S29–S38. - PubMed
-
- Caughman SW, Li LJ, Degitz K. (1990) Characterization and functional analysis of interferon-gamma-induced intercellular adhesion molecule-1 expression in human keratinocytes and A-431 cells. Journal of Investigative Dermatology 94: 22S–26S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

