Inter- and intra-species variation in genome-wide gene expression of Drosophila in response to parasitoid wasp attack
- PMID: 28449654
- PMCID: PMC5406980
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3697-3
Inter- and intra-species variation in genome-wide gene expression of Drosophila in response to parasitoid wasp attack
Abstract
Background: Parasitoid resistance in Drosophila varies considerably, among and within species. An immune response, lamellocyte-mediated encapsulation, evolved in a subclade of Drosophila and was subsequently lost in at least one species within this subclade. While the mechanisms of resistance are fairly well documented in D. melanogaster, much less is known for closely related species. Here, we studied the inter- and intra-species variation in gene expression after parasitoid attack in Drosophila. We used RNA-seq after parasitization of four closely related Drosophila species of the melanogaster subgroup and replicated lines of D. melanogaster experimentally selected for increased resistance to gain insights into short- and long-term evolutionary changes.
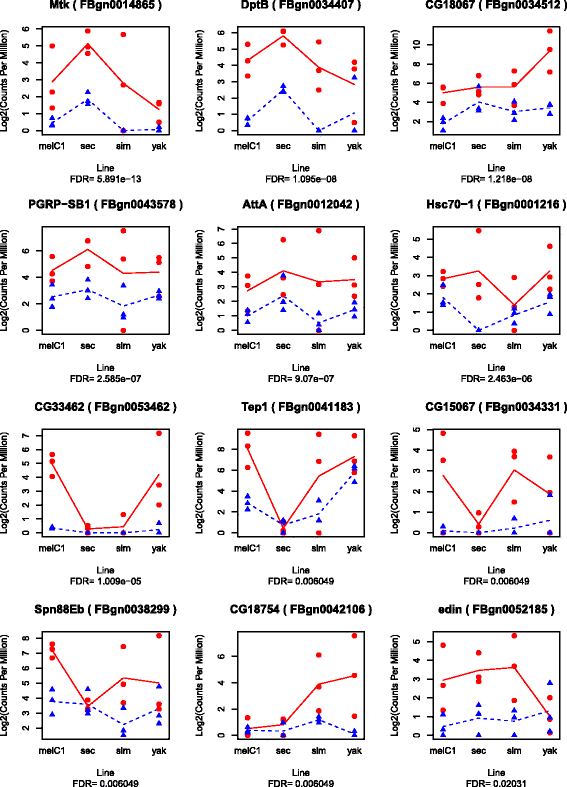
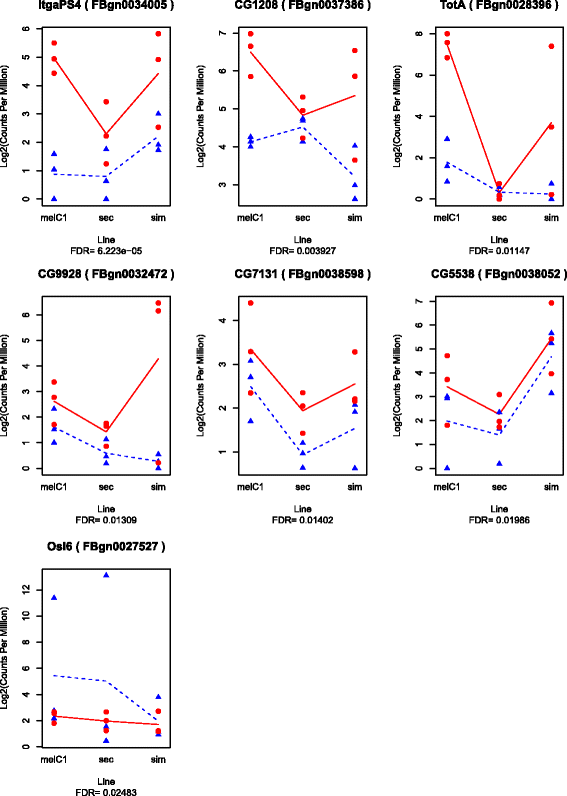
Results: We found a core set of genes that are consistently up-regulated after parasitoid attack in the species and lines tested, regardless of their level of resistance. Another set of genes showed no up-regulation or expression in D. sechellia, the species unable to raise an immune response against parasitoids. This set consists largely of genes that are lineage-restricted to the melanogaster subgroup. Artificially selected lines did not show significant differences in gene expression with respect to non-selected lines in their responses to parasitoid attack, but several genes showed differential exon usage.
Conclusions: We showed substantial similarities, but also notable differences, in the transcriptional responses to parasitoid attack among four closely related Drosophila species. In contrast, within D. melanogaster, the responses were remarkably similar. We confirmed that in the short-term, selection does not act on a pre-activation of the immune response. Instead it may target alternative mechanisms such as differential exon usage. In the long-term, we found support for the hypothesis that the ability to immunologically resist parasitoid attack is contingent on new genes that are restricted to the melanogaster subgroup.
Keywords: Drosophila speciesm; Evolution immune response; Parasitoid wasp; RNAseq.
Figures





Similar articles
-
High hemocyte load is associated with increased resistance against parasitoids in Drosophila suzukii, a relative of D. melanogaster.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e34721. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034721. Epub 2012 Apr 17. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22529929 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of a cellular immune response in Drosophila: a phenotypic and genomic comparative analysis.Genome Biol Evol. 2014 Feb;6(2):273-89. doi: 10.1093/gbe/evu012. Genome Biol Evol. 2014. PMID: 24443439 Free PMC article.
-
Does Drosophila sechellia escape parasitoid attack by feeding on a toxic resource?PeerJ. 2021 Jan 6;9:e10528. doi: 10.7717/peerj.10528. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 33505786 Free PMC article.
-
Variation of Leptopilina boulardi success in Drosophila hosts: what is inside the black box?Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:147-88. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70006-5. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773070 Review.
-
Evolution of host resistance and parasitoid counter-resistance.Adv Parasitol. 2009;70:257-80. doi: 10.1016/S0065-308X(09)70010-7. Adv Parasitol. 2009. PMID: 19773074 Review.
Cited by
-
Trans-regulatory changes underpin the evolution of the Drosophila immune response.PLoS Genet. 2022 Nov 7;18(11):e1010453. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010453. eCollection 2022 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36342922 Free PMC article.
-
Interactions with ectoparasitic mites induce host metabolic and immune responses in flies at the expense of reproduction-associated factors.Parasitology. 2020 Sep;147(11):1196-1205. doi: 10.1017/S0031182020000918. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Parasitology. 2020. PMID: 32498733 Free PMC article.
-
Host Transcriptome Analysis of Spodoptera frugiperda Larvae Parasitized by Microplitis manilae.Insects. 2023 Jan 17;14(2):100. doi: 10.3390/insects14020100. Insects. 2023. PMID: 36835669 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Read Genome Sequencing and Assembly of Leptopilina boulardi: A Specialist Drosophila Parasitoid.G3 (Bethesda). 2020 May 4;10(5):1485-1494. doi: 10.1534/g3.120.401151. G3 (Bethesda). 2020. PMID: 32217632 Free PMC article.
-
Candidate genes for shell colour polymorphism in Cepaea nemoralis.PeerJ. 2017 Sep 18;5:e3715. doi: 10.7717/peerj.3715. eCollection 2017. PeerJ. 2017. PMID: 28948095 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

