Clinical and demographic factors associated with change and maintenance of disease severity in a large registry of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28449692
- PMCID: PMC5406915
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1289-x
Clinical and demographic factors associated with change and maintenance of disease severity in a large registry of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: We examined models to predict disease activity transitions from moderate to low or severe and associated factors in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
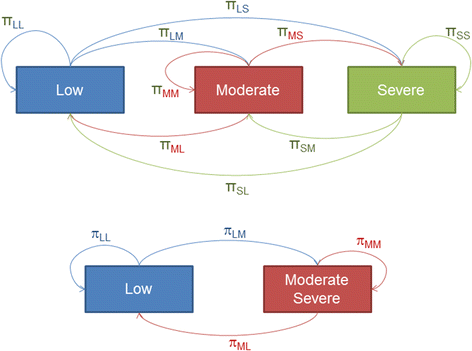
Methods: Data from RA patients enrolled in the Corrona registry (October 2001 to August 2014) were analyzed. Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) definitions were used for low (≤10), moderate (>10 and ≤22), and severe (>22) disease activity states. A Markov model for repeated measures allowing for covariate dependence was used to model transitions between three (low, moderate, severe) states and estimate population transition probabilities. Mean sojourn times were calculated to compare length of time in particular states. Logistic regression models were used to examine impacts of covariates (time between visits, chronological year, disease duration, age) on disease states.
Results: Data from 29,853 patients (251,375 visits) and a sub-cohort of 9812 patients (46,534 visits) with regular visits (every 3-9 months) were analyzed. The probability of moving from moderate to low or severe disease by next visit was 47% and 18%, respectively. Patients stayed in moderate disease for mean 4.25 months (95% confidence interval: 4.18-4.32). Transition probabilities showed 20% of patients with low disease activity moved to moderate or severe disease within 6 months; >35% of patients with moderate disease remained in moderate disease after 6 months. Results were similar for the regular-visit sub-cohort. Significant interactions with prior disease state were seen with chronological year and disease duration.
Conclusion: A substantial proportion of patients remain in moderate disease, emphasizing the need for treat-to-target strategies for RA patients.
Keywords: Clinical Disease Activity Index; Disease activity; Markov model; Prediction; Rheumatoid arthritis.
Figures
References
-
- Upchurch KS, Kay J. Evolution of treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51 Suppl 6:vi28–36. - PubMed
-
- Kievit W, Fransen J, Adang EM, den Broeder AA, Bernelot Moens HJ, Visser H, van de Laar MA, van Riel PL. Long-term effectiveness and safety of TNF-blocking agents in daily clinical practice: results from the Dutch Rheumatoid Arthritis Monitoring register. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2011;50(1):196–203. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/keq325. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Uhlig T, Lie E, Norvang V, Lexberg AS, Rodevand E, Kroll F, Kalstad S, Olsen IC, Kvien TK. Achievement of remission and low disease activity definitions in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: Results from the NOR-DMARD Study. J Rheumatol. 2016;43(4):716–23. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.151132. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

