Indistinguishable NDM-producing Escherichia coli isolated from recreational waters, sewage, and a clinical specimen in Ireland, 2016 to 2017
- PMID: 28449738
- PMCID: PMC5476983
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2017.22.15.30513
Indistinguishable NDM-producing Escherichia coli isolated from recreational waters, sewage, and a clinical specimen in Ireland, 2016 to 2017
Abstract
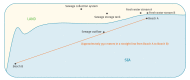
In this study, New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase (NDM)-producing Enterobacteriaceae were identified in Irish recreational waters and sewage. Indistinguishable NDM-producing Escherichia coli by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis were isolated from sewage, a fresh water stream and a human source. NDM-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from sewage and seawater in the same area were closely related to each other and to a human isolate. This raises concerns regarding the potential for sewage discharges to contribute to the spread of carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae.
Keywords: New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase; antimicrobial resistance; carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae; recreational waters; wastewater.
This article is copyright of The Authors, 2017.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Växjö: EUCAST. Version 7.0; 2017. Available from: http://www.eucast.org
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Multiplex real-time PCR detection of klebsiella pneumoniae carbapenemase (KPC) and new delhi metallo-β-lactamase (NDM-1) genes. Atlanta: CDC. 2011;6-7.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
