Intersection of diverse neuronal genomes and neuropsychiatric disease: The Brain Somatic Mosaicism Network
- PMID: 28450582
- PMCID: PMC5558435
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aal1641
Intersection of diverse neuronal genomes and neuropsychiatric disease: The Brain Somatic Mosaicism Network
Abstract
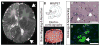
Neuropsychiatric disorders have a complex genetic architecture. Human genetic population-based studies have identified numerous heritable sequence and structural genomic variants associated with susceptibility to neuropsychiatric disease. However, these germline variants do not fully account for disease risk. During brain development, progenitor cells undergo billions of cell divisions to generate the ~80 billion neurons in the brain. The failure to accurately repair DNA damage arising during replication, transcription, and cellular metabolism amid this dramatic cellular expansion can lead to somatic mutations. Somatic mutations that alter subsets of neuronal transcriptomes and proteomes can, in turn, affect cell proliferation and survival and lead to neurodevelopmental disorders. The long life span of individual neurons and the direct relationship between neural circuits and behavior suggest that somatic mutations in small populations of neurons can significantly affect individual neurodevelopment. The Brain Somatic Mosaicism Network has been founded to study somatic mosaicism both in neurotypical human brains and in the context of complex neuropsychiatric disorders.
Copyright © 2017, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures
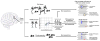

References
-
- Frank SA. Evolution in health and medicine Sackler colloquium: Somatic evolutionary genomics: Mutations during development cause highly variable genetic mosaicism with risk of cancer and neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(suppl 1):1725–1730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0909343106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 MH110558/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD079123/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106883/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106892/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH108898/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 MH019934/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS047101/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106884/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HG000040/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007753/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106891/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106876/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106882/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106893/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HD070494/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH100914/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090255/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007544/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 MH106874/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AG051791/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

