Modulation of gene expression dynamics by co-transcriptional histone methylations
- PMID: 28450734
- PMCID: PMC6130219
- DOI: 10.1038/emm.2017.19
Modulation of gene expression dynamics by co-transcriptional histone methylations
Abstract
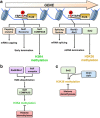
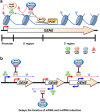
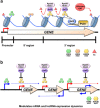
Co-transcriptional methylations of histone H3 at lysines 4 and 36, highly conserved methyl marks from yeast to humans, have profound roles in regulation of histone acetylation. These modifications function to recruit and/or activate distinct histone acetyltransferases (HATs) or histone deacetylases (HDACs). Whereas H3K4me3 increases acetylation at promoters via multiple HATs, H3K4me2 targets Set3 HDAC to deacetylate histones in 5' transcribed regions. In 3' regions of genes, H3K36me2/3 facilitates deacetylation by Rpd3S HDAC and slows elongation. Despite their important functions in deacetylation, no strong effects on global gene expression have been seen under optimized or laboratory growth conditions. Instead, H3K4me2-Set3 HDAC and Set2-Rpd3S pathways primarily delay the kinetics of messenger RNA (mRNA) and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) induction upon environmental changes. A majority of mRNA genes regulated by these pathways have an overlapping lncRNA transcription either from an upstream or an antisense promoter. Surprisingly, the distance between mRNA and lncRNA promoters seems to specify the repressive effects of the two pathways. Given that co-transcriptional methylations and acetylation have been linked to many cancers, studying their functions in a dynamic condition or during cancer progression will be much more important and help identify novel genes associated with cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell 2007; 128: 693–705. - PubMed
-
- Luger K, Mader AW, Richmond RK, Sargent DF, Richmond TJ. Crystal structure of the nucleosome core particle at 2.8A resolution. Nature 1997; 389: 251–260. - PubMed
-
- Workman JL, Kingston RE. Alteration of nucleosome structure as a mechanism of transcriptional regulation. Annu Rev Biochem 1998; 67: 545–579. - PubMed
-
- Li B, Carey M, Workman JL. The role of chromatin during transcription. Cell 2007; 128: 707–719. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

