Ellagic acid alleviates adjuvant induced arthritis by modulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines
- PMID: 28450796
- PMCID: PMC5382880
- DOI: 10.5114/ceji.2016.65132
Ellagic acid alleviates adjuvant induced arthritis by modulation of pro- and anti-inflammatory cytokines
Abstract
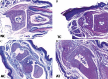
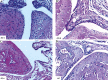
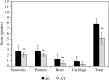
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disease of unknown aetiology, but it is now clear that pro-inflammatory cytokines play a central role in its pathogenesis. Ellagic acid (EA) has a variety of biological activities including anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-cancer properties. The aim of the present study was to evaluate the potential effect of ellagic acid on the prevention and/or treatment of adjuvant induced arthritis (AIA) model in mice. Ellagic acid treatment was started one week before AIA induction and continued for three weeks after induction of AIA. Ellagic acid treatment significantly (p < 0.01) inhibited foot paw oedematous swelling and attenuated AIA-associated pathology. Ellagic acid significantly (p < 0.01) reduced serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines: interleukin 1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), and interleukin 17 (IL-17). However, serum levels of IL-10 and interferon γ (IFN-γ) significantly increased (p < 0.01 and p < 0.05, respectively), while serum level of transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) did not significantly alter with EA treatment. In conclusion, these results suggest that EA attenuated AIA-associated pathology in the mouse model by downregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and upregulation of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
Keywords: adjuvant induced arthritis; anti-inflammatory cytokine; ellagic acid; pro-inflammatory cytokine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ibold Y, Frauenschuh S, Kaps C, et al. Development of a high-throughput screening assay based on the 3-dimensional pannus model for rheumatoid arthritis. J Biomol Screen. 2007;12:956–965. - PubMed
-
- Epstein FH, Choy EH, Panayi GS. Cytokine pathways and joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2001;344:907–916. - PubMed
-
- Majithia V, Geraci SA. Rheumatoid arthritis: diagnosis and management. Am J Med. 2007;120:936–939. - PubMed
-
- Choy E. Understanding the dynamics: pathways involved in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology. 2012;51:v3–v11. - PubMed
-
- Arend WP, Dayer JM. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukins-1 and tumor necrosis factor α in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995;38:151–160. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
