pATM and γH2AX are effective radiation biomarkers in assessing the radiosensitivity of 12C6+ in human tumor cells
- PMID: 28450809
- PMCID: PMC5405484
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-017-0419-5
pATM and γH2AX are effective radiation biomarkers in assessing the radiosensitivity of 12C6+ in human tumor cells
Abstract
Background: Tumour radiosensitivity would be particularly useful in optimizing the radiation dose during radiotherapy. The aim of the current study was to evaluate the potential value of phosphorylated H2AX (γH2AX) and ATM (pATM) in assessing 12C6+ radiosensitivity of tumour cells.
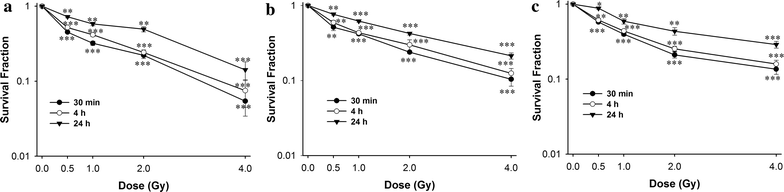
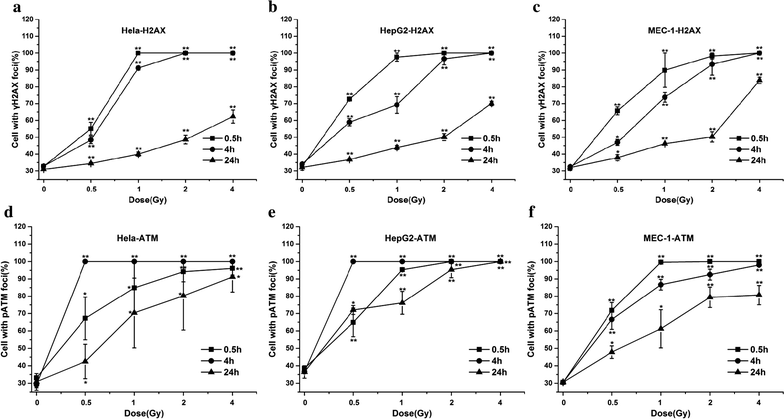
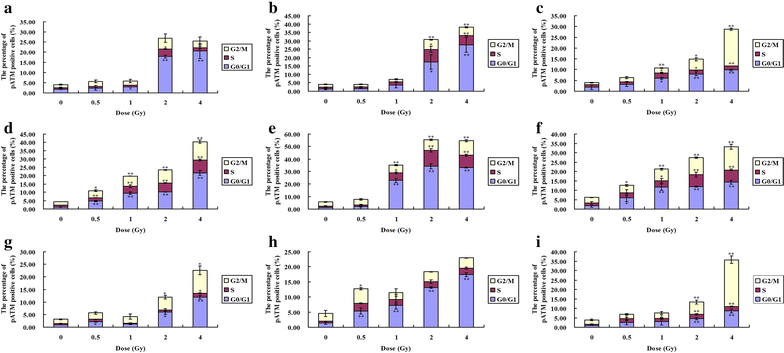
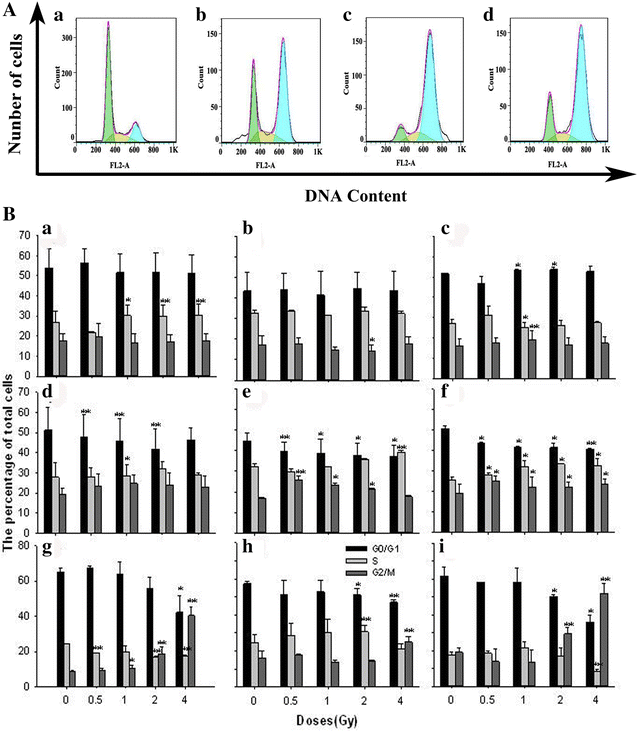
Methods: Human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, hepatoma HepG2 cells, and mucoepidermoid carcinoma MEC-1 cells were irradiated with different doses of 12C6+. The survival fraction was assayed with clonogenic survival method and the foci of γH2AX and pATM was visualized using immunocytochemical methods. Flow cytometry was used to assay γH2AX, pATM and the cell cycle.
Results: The survival fraction decreased immediately in dose-dependent manner, but in turn, significantly increased during 24 h after 12C6+ irradiation. Both γH2AX and pATM foci accumulated linearly with doses and with a maximum induction at 0.5 h for γH2AX and 0.5 or 4 h for pATM, respectively, and a fraction foci kept for 24 h. The expression of γH2AX and pATM was in relation to cell cycle. The G0/G1 phase cells had the highest expression of γH2AX after 0.5 h irradiation and then decreased to a lower level at 24 h after irradiation. An obvious increase of pATM in G2/M phase was shown after 24 h of 2 and 4 Gy irradiation. The significant G2/M phase arrest was shown. There was a close relationship between the clonogenic survival and γH2AX and pATM expression both in timing and dose in response to 12C6+.
Conclusions: The rate of γH2AX and pATM formation and loss may be an important factor in the response of cells to 12C6+. pATM and γH2AX are effective radiation biomarkers in assessing the radiosensitivity of 12C6+ in human tumor cells.
Keywords: 12C6+; ATM; Human tumor cells; Survival fraction; γH2AX.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The potential value of the neutral comet assay and γH2AX foci assay in assessing the radiosensitivity of carbon beam in human tumor cell lines.Radiol Oncol. 2013 Jul 30;47(3):247-57. doi: 10.2478/raon-2013-0045. eCollection 2013. Radiol Oncol. 2013. PMID: 24133390 Free PMC article.
-
Formation of γH2AX and pATM Foci in Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exposed to Low Dose-Rate Gamma-Radiation.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 May 29;20(11):2645. doi: 10.3390/ijms20112645. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31146367 Free PMC article.
-
Low doses of X-rays induce prolonged and ATM-independent persistence of γH2AX foci in human gingival mesenchymal stem cells.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):27275-87. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4739. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26314960 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Dose Hypersensitive Response for Residual pATM and γH2AX Foci in Normal Fibroblasts of Cancer Patients.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Mar 1;100(3):756-766. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2017.10.054. Epub 2017 Nov 6. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 29248168
-
Overview of radiosensitivity of human tumor cells to low-dose-rate irradiation.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008 Nov 1;72(3):909-17. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2008.06.1928. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008. PMID: 19014780 Review.
Cited by
-
MRN (MRE11-RAD50-NBS1) Complex in Human Cancer and Prognostic Implications in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Feb 14;20(4):816. doi: 10.3390/ijms20040816. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 30769804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A porous polyaniline nanotube sorbent for solid-phase extraction of the fluorescent reaction product of reactive oxygen species in cells, and its determination by HPLC.Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Sep 19;185(10):468. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-3000-6. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30232631
-
Involvement of HIF-1α in the Detection, Signaling, and Repair of DNA Double-Strand Breaks after Photon and Carbon-Ion Irradiation.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jul 30;13(15):3833. doi: 10.3390/cancers13153833. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34359734 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of X-ray and carbon-ion beam irradiation with chemotherapy for the treatment of cervical adenocarcinoma cells in 2D and 3D cultures.Cancer Cell Int. 2022 Dec 9;22(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02810-9. Cancer Cell Int. 2022. PMID: 36494817 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Effects of Monoenergetic Carbon Ions and Their Associated Secondary Particles.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 17;12:788293. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.788293. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35251969 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

