Langerhans' cell histiocytosis of the temporal bone: A case report
- PMID: 28450940
- PMCID: PMC5403409
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2017.4072
Langerhans' cell histiocytosis of the temporal bone: A case report
Abstract
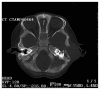
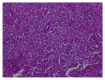
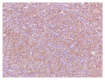
Langerhansmporal histiocytosis (LCH) refers to a group of diseases that are characterized by the primary pathogenesis of an abnormal polyclonal proliferation of Langerhans cells that affect different structures of the human body, including the temporal bone. Thus far, the etiology of LCH remains unclear. Diagnosis of LCH is based on a synthetic analysis of the clinical presentations, as well as on features of imaging and histopathology. The clinical features, diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of LCH remain obscure, and temporal LCH is often confused with ear inflammatory lesions and malignant tumors. There are several therapeutic modalities for temporal bone LCH that include surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and steroidal injections. The present study reports the case of an infant presenting a 1-month history of worsening left facial paralysis and a slowly enlarging post auricular mass followed by a 1-month history of postauricular swelling in the left ear. Computed tomography demonstrated a large mass of organized tissue. Moreover, the diagnosis of LCH was confirmed by histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations. The patient also suffered from multiple organ failure, including the liver, kidney, lymphatic system, skin, hematopoietic system and lungs. Following surgical intervention with mastoidotympanectomy, the parents of the patient refused further chemotherapy, and the patient succumbed to the disease ~6 months later.
Keywords: Langerhans' cell histiocytosis; diagnosis; etiology; mastoidotympanectomy; prognosis; temporal bone; therapeutic modalities.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
