Green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against dental pathogens
- PMID: 28452017
- PMCID: PMC5428112
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-017-0670-4
Green synthesis of silver oxide nanoparticles and its antibacterial activity against dental pathogens
Abstract
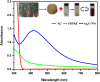
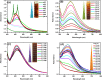
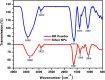
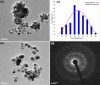
In the present study, the use of silver oxide nanoparticles (Ag2O NPs) synthesized using Ficus benghalensis prop root extract (FBPRE) as a reducing and stabilizing agent is reported and evaluated for its antibacterial activity against dental bacterial strains. The effects of pH, extract concentration, metal ion concentration, and contact time were studied to confirm the optimum production of Ag2O NPs. Our results suggest that, by increasing the extract concentration and the time frame, there will be a significant increase in the formation of nanoparticles. The UV-vis adsorption spectra show the absorbance peak in the range of 430 nm, and FTIR spectral peaks indicate that the phytochemicals in the extract are responsible for the formation of the nanoparticles. The HR-TEM image, SAED, and XRD pattern confirmed the morphology (spherical), silver oxide 42.7 nm and silver 51.4 nm, and crystalline nature of the obtained nanoparticles, respectively. The blend of FBPRE and Ag2O NPs showed excellent antibacterial activities against the two-dental bacteria Streptococcus mutans and Lactobacilli sp. The study results suggest that the blend of synthesized Ag2O NPS and FBPRE will be useful in tooth paste as a germicidal agent after extensive investigation with animal models.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Characterization; Ficus benghalensis; Nanoparticles; Optimization; Silver oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The author(s) declare(s) that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Bioengineered synthesis of phytochemical-adorned green silver oxide (Ag2O) nanoparticles via Mentha pulegium and Ficus carica extracts with high antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal activities.Sci Rep. 2022 Dec 13;12(1):21509. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-26021-4. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36513776 Free PMC article.
-
Studying the properties of green synthesized silver oxide nanoparticles in the application of organic dye degradation under visible light.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 6;14(1):26967. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-75614-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39505895 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrobacter sp. extract mediated biosynthesis of Ag2O NPs with excellent antioxidant and antibacterial potential for biomedical application.IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016 Dec;10(6):425-430. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2015.0097. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016. PMID: 27906145 Free PMC article.
-
Facile green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using seed aqueous extract of Pistacia atlantica and its antibacterial activity.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015 Jan 5;134:326-32. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2014.05.078. Epub 2014 Jun 19. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2015. PMID: 25022505
-
Ag2O Nanoparticles as a Candidate for Antimicrobial Compounds of the New Generation.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 5;15(8):968. doi: 10.3390/ph15080968. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015116 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synergistic effect of ZnO/Ag2O@g-C3N4 based nanocomposites embedded in carrageenan matrix for dye degradation in water.Heliyon. 2024 May 10;10(11):e31109. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31109. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38828361 Free PMC article.
-
Green Synthesis of Transition-Metal Nanoparticles and Their Oxides: A Review.Materials (Basel). 2021 May 21;14(11):2700. doi: 10.3390/ma14112700. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34063800 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural insights and biomedical potential of biosynthesized silver nanoparticles: antibacterial activity, anti-biofilm and cancer cell inhibition.PeerJ. 2025 Jul 1;13:e19608. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19608. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40620779 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Green Silver Nanoparticles Fabricated by Spirulina platensis Phycocyanin as Anticancer and Antimicrobial Agents.Life (Basel). 2022 Sep 26;12(10):1493. doi: 10.3390/life12101493. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36294927 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles as antimicrobial and antiviral agents: A literature-based perspective study.Heliyon. 2021 Mar 13;7(3):e06456. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06456. eCollection 2021 Mar. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 33763612 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahmad S, Rao H, Akhtar M, Ahmad I, Hayat MM, Iqbal Z. Phytochemical composition and pharmacological prospectus of Ficus bengalensis Linn. (Moraceae)-A review. J Med Plants Res. 2011;5:6393–6400.
-
- Ahmed S, Ahmad M, Swami BL, Ikram S. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using Azadirachta indica aqueous leaf extract. J Radiat Res Appl Sci. 2016;9:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jrras.2015.06.006. - DOI
-
- Amin M, Anwar F, Janjua MR, Iqbal MA, Rashid U. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles through reduction with Solanum xanthocarpum L. berry extract: characterization, antimicrobial and urease inhibitory activities against Helicobacter pylori. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13:9923–9941. doi: 10.3390/ijms13089923. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aswar M, Aswar U, Watkar B, Vyas M, Wagh A, Gujar K. Anthelmintic activity of Ficus benghalensis. Int J Green Pharm. 2008;2:170–172. doi: 10.4103/0973-8258.42737. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

