Structural characterization of folding intermediates in cytochrome c by H-exchange labelling and proton NMR
- PMID: 2845279
- PMCID: PMC3430852
- DOI: 10.1038/335700a0
Structural characterization of folding intermediates in cytochrome c by H-exchange labelling and proton NMR
Abstract
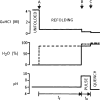
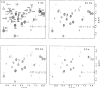
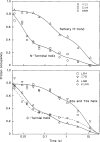
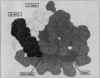
To understand the process of protein folding, it will be necessary to obtain detailed structural information on folding intermediates. This difficult problem is being studied by using hydrogen exchange and rapid mixing to label transient structural intermediates, with subsequent analysis of the proton-labelling pattern by two-dimensional nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Results for cytochrome c show that the method provides the spatial and temporal resolution necessary to monitor structure formation at many defined sites along the polypeptide chain on a timescale ranging from milliseconds to minutes.
Figures

References
-
- Kim PS, Baldwin RLA. Rev. Bioehem. 51:459–489. 9821.
-
- Creighton TE. Prog. Biophys. molec. Biol. 1978;33:231–297. - PubMed
-
- Schmid FX, Baldwin RL. J. molec. Biol. 1979;135:199–215. - PubMed
-
- Kim PS, Baldwin RL. Biochemistry. 1980;19:6124–6129. - PubMed
-
- Udgaonkar JB, Baldwin RL. Nature. 1988;335:694–699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

