An inverse association between tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk
- PMID: 28454102
- PMCID: PMC5514915
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.16959
An inverse association between tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk
Abstract
It is well known that the tea extracts, mainly polyphenols as chemo-preventive elements, could act as cancer progression blockers. Although the association between tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk has been widely investigated, the results still remain inconsistent. We conducted a dose-response meta-analysis to evaluate their relationships by enrolling qualified 29 literatures. The summary odds ratio (OR) of colorectal cancer for the highest vs. lowest tea consumption was 0.93 with 0.87-1.00 of 95% confidence intervals (CIs) among all studies with modest heterogeneity (P = 0.001, I2 = 43.4%). Stratified analysis revealed that tea, especially green tea, had a protective effect among female and rectal cancer patients. Particularly, the dose-response analysis showed that there was a significant inverse association between an increment of 1 cup/day of tea consumption and colorectal cancer risk in the subgroup of the green tea drinking (OR = 0.98, 95% CI = 0.96-1.01, Pnonlinear = 0.003) and female (OR = 0.68, 95% CI = 0.56-0.81, Pnonlinear < 0.001). Our findings indicate that tea consumption has an inverse impact on colorectal cancer risk, which may have significant public health implications in the prevention of colorectal cancer and further similar researches.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; inverse association; tea consumption.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing financial interest exists.
Figures

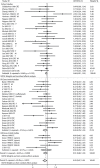
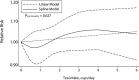
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, Parkin DM, Forman D, Bray F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. International journal of cancer. 2015;136:E359–386. - PubMed
-
- Siegel R, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2014. CA Cancer J Clin. 2014;64:9–29. - PubMed
-
- Hartman TJ, Tangrea JA, Pietinen P, Malila N, Virtanen M, Taylor PR, Albanes D. Tea and coffee consumption and risk of colon and rectal cancer in middle-aged Finnish men. Nutr Cancer. 1998;31:41–48. - PubMed
-
- Beltz LA, Bayer DK, Moss AL, Simet IM. Mechanisms of cancer prevention by green and black tea polyphenols. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2006;6:389–406. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

