Overexpression of heat-shock factor 1 is associated with a poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 28454329
- PMCID: PMC5403275
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.5637
Overexpression of heat-shock factor 1 is associated with a poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
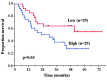
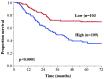
Heat-shock factor 1 (HSF1) is the primary regulator of the response to various stressors. A previous study showed that HSF1 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in breast cancer and hepatocellular carcinoma; however, the prognostic significance of HSF1 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is unknown. Therefore, the present study investigated the association between HSF1 expression and the clinicopathological parameters of patients, as well as the association between HSF1 expression, and heat shock protein (Hsp)27, Hsp70 and Hsp90 expression induced by HSF1, by cDNA microarray and immunohistochemistry analyses. HSF1 protein and mRNA expression were assessed in resected specimens from 270 patients with ESCC in two independent cohorts. Hsp27, Hsp70 and Hsp90 expression were also assessed in 55/270 patients. Patients with high HSF1 expression had a significantly worse OS than those with low HSF1 expression in both cohorts. In multivariate analyses, pathological T stage [hazard ratio (HR), 2.21; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.38-3.65; P=0.0008], pathological N stage (HR, 1.73; 95% CI, 1.04-3.02; P=0.03) and HSF1 expression (HR, 2.29; 95% CI, 1.48-3.64; P=0.0002) were statistically significant independent prognostic factors. Furthermore, Hsp27 and Hsp90 expression were significantly correlated with HSF1 expression (P<0.0001), but Hsp70 expression was not (P=0.38). These results indicate that HSF1 is a prognostic factor for patients with ESCC, and that Hsp27 and Hsp90, but not Hsp70, may be the downstream targets of HSF1 in ESCC.
Keywords: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; heat-shock factor 1; prognosis.
Figures


References
-
- Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK, Wittekind Ch, editors. TNM Classification of Malignant Tumors. 7th. Wiley-Blackwell; Oxford: 2009. Oesophagus including oesophagogastric junction; pp. 65–72.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
