MicroRNA-134 targets KRAS to suppress breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion
- PMID: 28454346
- PMCID: PMC5403703
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.5644
MicroRNA-134 targets KRAS to suppress breast cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion
Abstract
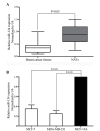
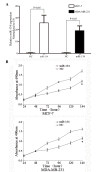
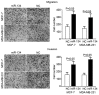
The expression patterns and functions of microRNA-134 (miR-134) have been previously studied in numerous types of cancer. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study of miR-134 in human breast cancer. In the present study, the expression patterns, biological functions and underlying molecular mechanisms of miR-134 in human breast cancer were investigated. Reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction evaluated the expression of miR-134 in human breast cancer tissues, matched normal adjacent tissues, breast cancer cell lines and a normal mammary epithelial cell line. Following transfection with miR-134, an MTT assay, cell migration assay, cell invasion assay, western blot analysis and a luciferase assay were performed on the MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cell lines. The findings revealed that miR-134 expression levels were significantly downregulated in breast cancer cells. Statistical analysis demonstrated that low expression of miR-134 was significantly associated with lymph node metastasis, TNM stage and reduced cell differentiation. It was observed that miR-134 inhibited the growth, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Additionally, the present study indicated that miR-134 may directly target the Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog in breast cancer tissues. These results suggest that miR-134 may be used as a potential therapeutic biomarker in breast cancers.
Keywords: Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog; breast cancer; microRNA-134; therapy.
Figures

Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-421 inhibits breast cancer metastasis by targeting metastasis associated 1.Biomed Pharmacother. 2016 Oct;83:1398-1406. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.08.058. Epub 2016 Aug 29. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016. PMID: 27583980
-
MicroRNA 217 inhibits cell proliferation and enhances chemosensitivity to doxorubicin in acute myeloid leukemia by targeting KRAS.Oncol Lett. 2017 Jun;13(6):4986-4994. doi: 10.3892/ol.2017.6076. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Oncol Lett. 2017. PMID: 28599501 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-9 promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of breast cancer cells via down-regulating FOXO1.Clin Transl Oncol. 2017 Sep;19(9):1133-1140. doi: 10.1007/s12094-017-1650-1. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Clin Transl Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28397066
-
In vivo and in vitro effects of microRNA-27a on proliferation, migration and invasion of breast cancer cells through targeting of SFRP1 gene via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 28;8(9):15507-15519. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14662. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28099945 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-623 inhibits tumor progression and is a predictor of poor prognosis of breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2020 Dec;20(6):386. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.12249. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 33193846 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA-134 prevents the progression of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma via the PLXNA1-mediated MAPK signalling pathway.EBioMedicine. 2019 Aug;46:66-78. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.050. Epub 2019 Aug 2. EBioMedicine. 2019. Retraction in: EBioMedicine. 2024 May;103:105105. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2024.105105. PMID: 31383552 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Prognostic role of 14q32.31 miRNA cluster in various carcinomas: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020 Feb;37(1):31-46. doi: 10.1007/s10585-019-10013-2. Epub 2019 Dec 7. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2020. PMID: 31813069
-
Recent developments in targeting breast cancer stem cells (BCSCs): a descriptive review of therapeutic strategies and emerging therapies.Med Oncol. 2024 Apr 9;41(5):112. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02347-z. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38592510 Review.
-
miR-202 acts as a potential tumor suppressor in breast cancer.Oncol Lett. 2018 Jul;16(1):1155-1162. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.8726. Epub 2018 May 16. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29963190 Free PMC article.
-
Ruyiping formula inhibits metastasis via the microRNA-134-SLUG axis in breast cancer.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jul 5;21(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03365-4. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 34225726 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
