Increased B7-H4 expression during esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis is associated with IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway activation in mice
- PMID: 28454382
- PMCID: PMC5403357
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.5688
Increased B7-H4 expression during esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis is associated with IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway activation in mice
Abstract
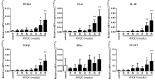
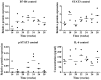
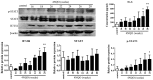
B7-homolog 4 (B7-H4), one of the costimulatory molecules of the B7 family, has been reported to be widely expressed in multiple types of cancer tissues, and to be important in tumor progression and poor prognosis. However, the role of B7-H4 in esophageal precancerous lesions has not been elucidated yet. In the present study, a model of esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis was established in 208 C57BL/6 mice by 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide (4NQO) drinking water of mice, and the changes in the expression of B7-H4 during the whole pathological process were investigated. Hematoxylin and eosin staining results demonstrated that the pathological stage was exacerbated with the increase in time of 4NQO-mediated carcinogenesis induction, and the pathological features were similar to those observed in humans. Immunohistochemistry results revealed that B7-H4 expression was upregulated and positively correlated with pathological stage (P<0.0001) as well as with infiltration of cluster of differentiation (CD) 11b+ macrophage cells (P=0.0002). In addition, B7-H4 messenger RNA expression increased in the esophagi of model mice compared with that of control mice, which was positively associated with the gene expression of interleukin (IL)-6 and signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), according to the results of reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis. Similarly, B7-H4 protein expression was upregulated in the esophageal tissues of model mice in comparison with that of control mice, and was positively associated with IL-6 expression and STAT3 phosphorylation. In conclusion, the present data suggested that B7-H4 expression increased during esophageal squamous cell carcinogenesis in mice in association with IL-6/STAT3 signaling pathway activation.
Keywords: 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide; B7-homolog 4; esophageal carcinogenesis; interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling pathway; precancerous condition.
Figures



Similar articles
-
B7-H4 facilitates proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells through promoting interleukin-6/signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 pathway activation.Cancer Sci. 2016 Jul;107(7):944-54. doi: 10.1111/cas.12949. Epub 2016 May 27. Cancer Sci. 2016. PMID: 27088889 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of coinhibitory molecules B7-H3 and B7-H4 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Tumour Biol. 2016 Mar;37(3):2961-71. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4132-5. Epub 2015 Sep 28. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26411671
-
Negative roles of B7-H3 and B7-H4 in the microenvironment of cervical cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2018 Oct 1;371(1):222-230. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.08.014. Epub 2018 Aug 9. Exp Cell Res. 2018. PMID: 30099052
-
B7-H4(B7x)-Mediated Cross-talk between Glioma-Initiating Cells and Macrophages via the IL6/JAK/STAT3 Pathway Lead to Poor Prognosis in Glioma Patients.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 1;22(11):2778-2790. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0858. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27001312 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of combined expression of B7-H3 and B7-H4 as prognostic marker in esophageal cancer patients.Oncotarget. 2016 Nov 22;7(47):77237-77243. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.12628. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27764786 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of B7-H4 promotes renal cell carcinoma progression by recruiting tumor-associated neutrophils via upregulation of CXCL8.Oncol Lett. 2020 Aug;20(2):1535-1544. doi: 10.3892/ol.2020.11701. Epub 2020 Jun 5. Oncol Lett. 2020. PMID: 32724395 Free PMC article.
-
[Effect of thoraco-laparoscopic esophagectomy on postoperative immune function of patients with esophageal carcinoma].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021 Jan 30;41(1):146-150. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2021.01.22. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2021. PMID: 33509768 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
B7H4 Role in Solid Cancers: A Review of the Literature.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 11;16(14):2519. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142519. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aberrant expression of B7-H4 and B7-H5 contributes to the development of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Arch Dermatol Res. 2024 Jun 8;316(7):382. doi: 10.1007/s00403-024-03095-w. Arch Dermatol Res. 2024. PMID: 38850312 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Herszényi L, Tulassay Z. Epidemiology of gastrointestinal and liver tumors. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2010;14:249–258. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
