Ethanolic extract of Thevetia peruviana flowers enhances TNF-α and TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells via intrinsic and extrinsic pathways
- PMID: 28454468
- PMCID: PMC5403174
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2017.5748
Ethanolic extract of Thevetia peruviana flowers enhances TNF-α and TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human cervical cancer cells via intrinsic and extrinsic pathways
Abstract
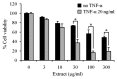
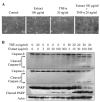
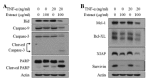
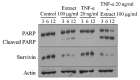
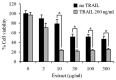
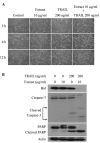
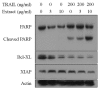
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) are promising candidates for cancer treatment due to their ability to induce apoptosis through death receptor stimulation. However, their usage may be limited due to the resistance of cancer cells to TNF-α- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Currently, there is interest in screening for natural products that can sensitize cancer cells to TNF-α- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis for their use in combination with TNF-α or TRAIL. It was previously reported that the bark extract of Thevetia peruviana showed a reversal effect on TRAIL-resistance in human gastric adenocarcinoma cell lines. In the present study, the effects of the ethanolic extract of T. peruviana flowers on TNF-α- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis of human cervical cancer HeLa cells were investigated in vitro by determining cell viability and apoptosis using a WST-1 cell proliferation assay and immunoblot analysis, respectively. The ethanolic extract of T. peruviana flowers promoted TNF-α and TRAIL-mediated cell death through the activation of the caspase cascade, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase and BH3-interacting domain death agonist cleavage. Combined treatment using the extract plus TNF-α resulted in downregulation of anti-apoptotic protein, including myeloid cell leukemia sequence-1, B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-XL), X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein and survivin, while the combined treatment with TRAIL downregulated Bcl-XL. Thus, the ethanolic extract of T. peruviana flowers has potential in sensitizing the TNF-α- and TRAIL-induced apoptosis of HeLa cells via the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways.
Keywords: B-cell lymphoma-extra large; HeLa cells; anti-apoptotic protein; cardiac glycosides; cervical cancer; death receptor; plant extract.
Figures
References
-
- Morales-Cano D, Calviño E, Rubio V, Herráez A, Sancho P, Tejedor MC, Diez JC. Apoptosis induced by paclitaxel via Bcl-2, Bax and caspases 3 and 9 activation in NB4 human leukaemia cells is not modulated by ERK inhibition. Exp Toxicol Pathol. 2013;65:1101–1108. doi: 10.1016/j.etp.2013.04.006. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Huang CR, Jin ZX, Dong L, Tong XP, Yue S, Kawanami T, Sawaki T, Sakai T, Miki M, Iwao H, et al. Cisplatin augments FAS-mediated apoptosis through lipid rafts. Anticancer Res. 2010;30:2065–2071. - PubMed
-
- Lee HH, Ye S, Li XJ, Lee KB, Park MH, Kim SM. Combination treatment with paclitaxel and doxorubicin inhibits growth of human esophageal squamous cancer cells by inactivation of Akt. Oncol Rep. 2014;31:183–188. - PubMed
-
- Kim CW, Lu JN, Go SI, Jung JH, Yi SM, Jeong JH, Hah YS, Han MS, Park JW, Lee WS, Min YJ. P53 restoration can overcome cisplatin resistance through inhibition of Akt as well as induction of Bax. Int J Oncol. 2013;43:1495–1502. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
