Complement C5aR1 Signaling Promotes Polarization and Proliferation of Embryonic Neural Progenitor Cells through PKCζ
- PMID: 28455369
- PMCID: PMC6596536
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0525-17.2017
Complement C5aR1 Signaling Promotes Polarization and Proliferation of Embryonic Neural Progenitor Cells through PKCζ
Abstract
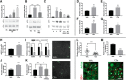
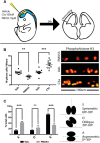
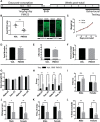
The complement system, typically associated with innate immunity, is emerging as a key controller of nonimmune systems including in development, with recent studies linking complement mutations with neurodevelopmental disease. A key effector of the complement response is the activation fragment C5a, which, through its receptor C5aR1, is a potent driver of inflammation. Surprisingly, C5aR1 is also expressed during early mammalian embryogenesis; however, no clearly defined function is ascribed to C5aR1 in development. Here we demonstrate polarized expression of C5aR1 on the apical surface of mouse embryonic neural progenitor cells in vivo and on human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors. We also show that signaling of endogenous C5a during mouse embryogenesis drives proliferation of neural progenitor cells within the ventricular zone and is required for normal brain histogenesis. C5aR1 signaling in neural progenitors was dependent on atypical protein kinase C ζ, a mediator of stem cell polarity, with C5aR1 inhibition reducing proliferation and symmetric division of apical neural progenitors in human and mouse models. C5aR1 signaling was shown to promote the maintenance of cell polarity, with exogenous C5a increasing the retention of polarized rosette architecture in human neural progenitors after physical or chemical disruption. Transient inhibition of C5aR1 during neurogenesis in developing mice led to behavioral abnormalities in both sexes and MRI-detected brain microstructural alterations, in studied males, demonstrating a requirement of C5aR1 signaling for appropriate brain development. This study thus identifies a functional role for C5a-C5aR1 signaling in mammalian neurogenesis and provides mechanistic insight into recently identified complement gene mutations and brain disorders.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The complement system, traditionally known as a controller of innate immunity, now stands as a multifaceted signaling family with a broad range of physiological actions. These include roles in the brain, where complement activation is associated with diseases, including epilepsy and schizophrenia. This study has explored complement regulation of neurogenesis, identifying a novel relationship between the complement activation peptide C5a and the neural progenitor proliferation underpinning formation of the mammalian brain. C5a was identified as a regulator of cell polarity, with inhibition of C5a receptors during embryogenesis leading to abnormal brain development and behavioral deficits. This work demonstrates mechanisms through which dysregulation of complement causes developmental disease and highlights the potential risk of complement inhibition for therapeutic purposes in pregnancy.
Keywords: C5a; C5aR1; aPKC; complement; neurogenesis; polarity.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/375396-13$15.00/0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Complement C3a receptor modulates embryonic neural progenitor cell proliferation and cognitive performance.Mol Immunol. 2018 Sep;101:176-181. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.06.271. Epub 2018 Jun 27. Mol Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30449309
-
Complement C5a Receptor 1 Exacerbates the Pathophysiology of N. meningitidis Sepsis and Is a Potential Target for Disease Treatment.mBio. 2018 Jan 23;9(1):e01755-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01755-17. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29362231 Free PMC article.
-
C5a Increases the Injury to Primary Neurons Elicited by Fibrillar Amyloid Beta.ASN Neuro. 2017 Feb;9(1):1759091416687871. doi: 10.1177/1759091416687871. ASN Neuro. 2017. PMID: 28078911 Free PMC article.
-
The critical role of C5a as an initiator of neutrophil-mediated autoimmune inflammation of the joint and skin.Semin Immunol. 2018 Jun;37:21-29. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2018.03.002. Epub 2018 Mar 27. Semin Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29602515 Review.
-
The Complement Receptor C5aR2: A Powerful Modulator of Innate and Adaptive Immunity.J Immunol. 2019 Jun 15;202(12):3339-3348. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1900371. J Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31160390 Review.
Cited by
-
The Complement System: A Powerful Modulator and Effector of Astrocyte Function in the Healthy and Diseased Central Nervous System.Cells. 2021 Jul 17;10(7):1812. doi: 10.3390/cells10071812. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34359981 Free PMC article. Review.
-
C5aR1-positive adipocytes mediate non-shivering thermogenesis in neonatal mice.iScience. 2024 Oct 28;27(12):111261. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111261. eCollection 2024 Dec 20. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39758991 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Immune Factors in Shaping Fetal Neurodevelopment.Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 6;36:441-468. doi: 10.1146/annurev-cellbio-021120-033518. Epub 2020 Jul 28. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32722920 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cd59 and inflammation regulate Schwann cell development.Elife. 2022 Jun 24;11:e76640. doi: 10.7554/eLife.76640. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35748863 Free PMC article.
-
Significance of Complement System in Ischemic Stroke: A Comprehensive Review.Aging Dis. 2019 Apr 1;10(2):429-462. doi: 10.14336/AD.2019.0119. eCollection 2019 Apr. Aging Dis. 2019. PMID: 31011487 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Briggs JA, Sun J, Shepherd J, Ovchinnikov DA, Chung TL, Nayler SP, Kao LP, Morrow CA, Thakar NY, Soo SY, Peura T, Grimmond S, Wolvetang EJ (2013) Integration-free induced pluripotent stem cells model genetic and neural developmental features of Down syndrome etiology. Stem Cells 31:467–478. 10.1002/stem.1297 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
