Impact of RNA structure on ZFP36L2 interaction with luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA
- PMID: 28455422
- PMCID: PMC5513066
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.060467.116
Impact of RNA structure on ZFP36L2 interaction with luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA
Abstract
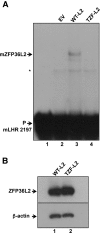
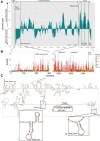
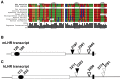
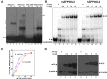
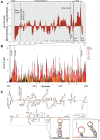
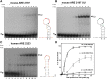
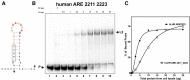
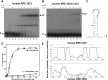
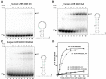
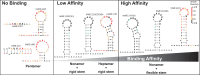
ZFP36L2 (L2) destabilizes AU-rich element (ARE)-containing transcripts and has been implicated in female fertility. We have shown that only one of three putative AREs within the 3' UTR of murine luteinizing hormone receptor mRNA, ARE2197 (UAUUUAU), is capable of interacting with L2. To assess whether structural elements of ARE2197 could explain this unique binding ability, we performed whole-transcript SHAPE-MaP (selective 2' hydroxyl acylation by primer extension-mutational profiling) of the full-length mLHR mRNA. The data revealed that the functional ARE2197 is located in a hairpin loop structure and most nucleotides are highly reactive. In contrast, each of the nonbinding AREs, 2301 and 2444, contains only a pentamer AUUUA; and in ARE2301 much of the ARE sequence is poorly accessible. Because the functional mARE was also found to be conserved in humans at the sequence level (ARE 2223), we decided to investigate whether binding and structure are also preserved. Similar to mouse, only one ARE in hLHR mRNA is capable of binding to L2; and it is also located in a hairpin structure, based on our SHAPE-MaP data. To investigate the role of secondary structure in the binding, we mutated specific nucleotides in both functional AREs. Mutations in the flexible stem region proximal to the loop that enforce strong base-pairing, drastically reduced L2 binding affinity; this confirms that the structural context is critical for L2 recognition of hARE2223. Collectively, our results suggest that a combination of minimal ARE sequence, placement of the ARE in a hairpin loop, and stem flexibility mediate high-affinity L2 binding to hLHR mRNA.
Keywords: LHR mRNA; RNA-binding protein; ZFP36L2; infertility; post-transcriptional modulation.
© 2017 Ball et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press for the RNA Society.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequence and tissue targeting specificity of ZFP36L2 reveals Elavl2 as a novel target with co-regulation potential.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):4068-4082. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac209. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35380695 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA-binding protein, ZFP36L2, influences ovulation and oocyte maturation.PLoS One. 2014 May 15;9(5):e97324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097324. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24830504 Free PMC article.
-
Phylogenetic distribution and evolution of the linked RNA-binding and NOT1-binding domains in the tristetraprolin family of tandem CCCH zinc finger proteins.J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014 Apr;34(4):297-306. doi: 10.1089/jir.2013.0150. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014. PMID: 24697206 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tristetraprolin inhibits poly(A)-tail synthesis in nuclear mRNA that contains AU-rich elements by interacting with poly(A)-binding protein nuclear 1.PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041313. Epub 2012 Jul 26. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22844456 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple functions of tristetraprolin/TIS11 RNA-binding proteins in the regulation of mRNA biogenesis and degradation.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013 Jun;70(12):2031-44. doi: 10.1007/s00018-012-1150-y. Epub 2012 Sep 12. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013. PMID: 22968342 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RNA-Binding Protein ZFP36L2 Downregulates Helios Expression and Suppresses the Function of Regulatory T Cells.Front Immunol. 2020 Jun 23;11:1291. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01291. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32655569 Free PMC article.
-
Visualization of lncRNA and mRNA Structure Models Within the Integrative Genomics Viewer.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2254:15-25. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1158-6_2. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33326067 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence and tissue targeting specificity of ZFP36L2 reveals Elavl2 as a novel target with co-regulation potential.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Apr 22;50(7):4068-4082. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac209. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 35380695 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Evidence of Translational Control by AU-Rich Element-Binding Proteins.Front Genet. 2019 May 2;10:332. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00332. eCollection 2019. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 31118942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Guidelines for SHAPE Reagent Choice and Detection Strategy for RNA Structure Probing Studies.Biochemistry. 2019 Jun 11;58(23):2655-2664. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b01218. Epub 2019 May 30. Biochemistry. 2019. PMID: 31117385 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
