Accuracy of testing for anti- Helicobacter pylori IgG in urine for H. pylori infection diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 28455424
- PMCID: PMC5719657
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013248
Accuracy of testing for anti- Helicobacter pylori IgG in urine for H. pylori infection diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: This meta-analysis aims to systematically measure the potential diagnostic value of anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG in urine for infection diagnosis, using all eligible studies published in English and Chinese languages.
Design: The random effect model was used to analyse the pooled sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio (PLR), negative LR (NLR), diagnostic OR (DOR), together with the summary receiver operator characteristic curve.
Setting: Literature searches of databases including PubMed, EMBASE, MEDLINE, Web of Science, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure and Wanfang databases were performed to retrieve studies evaluating the diagnostic value of urine IgG antibody for H.pylori infection.
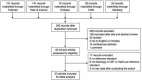
Primary outcome measure: Twenty-three studies with 4963 subjects were included in the current meta-analysis.
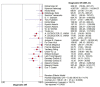
Results: The pooled sensitivity, specificity, PLR, NLR, DOR and area under the curve (AUC) were 0.83 (95% CI 0.82 to 0.85), 0.89 (95% CI 0.88 to 0.90), 8.81 (95% CI 6.37 to 12.2), 0.13 (95% CI 0.09 to 0.2), 73 (95% CI 46.45 to 114.74) and 0.9551, respectively. Subgroup analyses showed that diagnostic accuracy of the urine IgG assay was no different in age, region, study population and assay method.
Conclusions: Anti-H. pylori antibody in urine might serve as a good marker in diagnosing H. pylori infection. However, further validation based on a larger sample is still required.
Keywords: H.pylori; Meta analysis; diagnosis; urine IgG antibody.
© Article author(s) (or their employer(s) unless otherwise stated in the text of the article) 2017. All rights reserved. No commercial use is permitted unless otherwise expressly granted.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Non-invasive diagnostic tests for Helicobacter pylori infection.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Mar 15;3(3):CD012080. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012080.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29543326 Free PMC article.
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11(11):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 36394900 Free PMC article.
-
13C-Urea Breath Test for the Diagnosis of H. pylori Infection in Patients after Partial Gastrectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Invest Surg. 2022 May;35(5):1125-1134. doi: 10.1080/08941939.2021.1972185. Epub 2021 Sep 7. J Invest Surg. 2022. PMID: 34493140
-
Utility of stool sample-based tests for the diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection in children.J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011 Jun;52(6):718-28. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e3182077d33. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2011. PMID: 21478757
Cited by
-
Detecting anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in urine samples: A noninvasive and sensitive way to assay COVID-19 immune conversion.Sci Adv. 2022 May 13;8(19):eabn7424. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn7424. Epub 2022 May 13. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 35559681 Free PMC article.
-
Diet and rosacea: the role of dietary change in the management of rosacea.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017 Oct 31;7(4):31-37. doi: 10.5826/dpc.0704a08. eCollection 2017 Oct. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2017. PMID: 29214107 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenesis and clinical management of Helicobacter pylori gastric infection.World J Gastroenterol. 2019 Oct 7;25(37):5578-5589. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i37.5578. World J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31602159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Eradication efficacy of high-dose amoxicillin and proton pump inhibitor compared with quadruple therapy contained bismuth in the treatment of Helicobacter pylori.J Family Med Prim Care. 2022 Dec;11(12):7806-7809. doi: 10.4103/jfmpc.jfmpc_1035_22. Epub 2023 Jan 17. J Family Med Prim Care. 2022. PMID: 36994069 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic approach to Helicobacter pylori-related gastric oncogenesis.Ann Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul-Aug;35(4):333-344. doi: 10.20524/aog.2022.0725. Epub 2022 Jun 2. Ann Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 35784633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
