Genome editing in the mushroom-forming basidiomycete Coprinopsis cinerea, optimized by a high-throughput transformation system
- PMID: 28455526
- PMCID: PMC5430836
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-00883-5
Genome editing in the mushroom-forming basidiomycete Coprinopsis cinerea, optimized by a high-throughput transformation system
Abstract
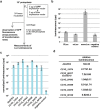
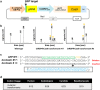
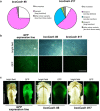
Mushroom-forming basidiomycetes produce a wide range of metabolites and have great value not only as food but also as an important global natural resource. Here, we demonstrate CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing in the model species Coprinopsis cinerea. Using a high-throughput reporter assay with cryopreserved protoplasts, we identified a novel promoter, CcDED1 pro , with seven times stronger activity in this assay than the conventional promoter GPD2. To develop highly efficient genome editing using CRISPR/Cas9 in C. cinerea, we used the CcDED1 pro to express Cas9 and a U6-snRNA promoter from C. cinerea to express gRNA. Finally, CRISPR/Cas9-mediated GFP mutagenesis was performed in a stable GFP expression line. Individual genome-edited lines were isolated, and loss of GFP function was detected in hyphae and fruiting body primordia. This novel method of high-throughput CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing using cryopreserved protoplasts should be a powerful tool in the study of edible mushrooms.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
CRISPR/Cas9-mediated efficient genome editing via protoplast-based transformation in yeast-like fungus Aureobasidium pullulans.Gene. 2019 Aug 15;709:8-16. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.04.079. Epub 2019 May 25. Gene. 2019. PMID: 31132514
-
Improved CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing by fluorescence activated cell sorting of green fluorescence protein tagged protoplasts.BMC Biotechnol. 2019 Jun 17;19(1):36. doi: 10.1186/s12896-019-0530-x. BMC Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31208390 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Genome Editing of Trichoderma reesei.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2234:87-98. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1048-0_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33165782
-
Genome editing tools based improved applications in macrofungi.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jul 30;51(1):873. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09809-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39080117 Review.
-
CRISPR/Cas9-based genome editing of the filamentous fungi: the state of the art.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017 Oct;101(20):7435-7443. doi: 10.1007/s00253-017-8497-9. Epub 2017 Sep 8. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28887634 Review.
Cited by
-
Edible and medicinal fungi breeding techniques, a review: Current status and future prospects.Curr Res Food Sci. 2022 Oct 17;5:2070-2080. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2022.09.002. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Food Sci. 2022. PMID: 36387595 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient CRISPR/Cas9 system based on autonomously replicating plasmid with an AMA1 sequence and precisely targeted gene deletion in the edible fungus, Cordyceps militaris.Microb Biotechnol. 2022 Oct;15(10):2594-2606. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.14107. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Microb Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35829671 Free PMC article.
-
CRISPR/Cas9 using a transient transformation system in Ceriporiopsis subvermispora.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(17):5575-5585. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12095-7. Epub 2022 Jul 29. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35902408
-
Improvement of genome editing efficiency by Cas9 codon optimization in Japanese cedar (Cryptomeria japonica D. Don).Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2024 Dec 25;41(4):335-344. doi: 10.5511/plantbiotechnology.24.0709a. Plant Biotechnol (Tokyo). 2024. PMID: 40083578 Free PMC article.
-
Preassembled Cas9 Ribonucleoprotein-Mediated Gene Deletion Identifies the Carbon Catabolite Repressor and Its Target Genes in Coprinopsis cinerea.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022 Dec 13;88(23):e0094022. doi: 10.1128/aem.00940-22. Epub 2022 Nov 14. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36374019 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

