Boschniakia Rossica Polysaccharide Triggers Laryngeal Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis by Regulating Expression of Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and P53
- PMID: 28455995
- PMCID: PMC5421584
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.901381
Boschniakia Rossica Polysaccharide Triggers Laryngeal Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis by Regulating Expression of Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and P53
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Boschniakia rossica Polysaccharide Triggers Laryngeal Carcinoma Cell Apoptosis by Regulating Expression of Bcl-2, Caspase-3, and P53.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Oct 7;30:e946770. doi: 10.12659/MSM.946770. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 39370918 Free PMC article.
Abstract
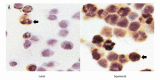
BACKGROUND Laryngeal cancer is a malignant head and neck tumor with high morbidity and high mortality in humans. Recently, treatments with Chinese medicines and their extracts have gradually received great attention, and studies suggest that Boschniakia rossica polysaccharide (BRP) has potential anti-tumor activity. Therefore, this study investigating the role of BRP in inducing apoptosis in human laryngeal carcinoma cells. MATERIAL AND METHODS The BRP was extracted with organic solvent and HR column. We treated Hep2 laryngeal carcinoma cells with different concentrations of BRP, then assessed cell growth inhibition rate by flow cytometry and apoptosis index by TUNEL staining. The protein expression of p53, Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3 were analyzed by Western blot. RESULTS Flow cytometry results showed that BRP inhibited Hep2 cell proliferation in a dose-dependent manner (p<0.05), and TUNEL staining indicated that BRP significantly increased Hep2 apoptosis index (p<0.05). Western blot results showed that the expression levels of p53 and activation of caspase-3 in Hep2 cells were significantly up-regulated (p<0.05), while the expression of Bcl-2 was significantly down-regulated (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS BRP might induce cell apoptosis by regulating the expression level of cell apoptosis-associated proteins, suggesting strong anti-laryngeal cancer activity.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures


References
-
- Patridge E, Gareiss P, Kinch MS, et al. An analysis of FDA-approved drugs: Natural products and their derivatives. Drug Discov Today. 2015;21(2):204–7. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Zheng S, Willingham MC, et al. [Mechanism of taxol-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells]. Chinese Journal of Cancer Research. 2013;10(1):32–36. [in Chinese] - PubMed
-
- Axelrod MJ, Fowles P, Silverman J, et al. The combination of entospletinib and vincristine demonstrates synergistic activity in a broad panel of hematological cancer cell lines and anti-tumor efficacy in a DLBCL xenograft model. Blood. 2015;126(23):5123.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

