Chronic intermittent hypoxia worsens bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats
- PMID: 28456608
- PMCID: PMC5659967
- DOI: 10.1016/j.resp.2017.04.010
Chronic intermittent hypoxia worsens bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats
Abstract
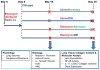
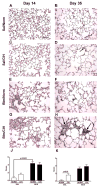
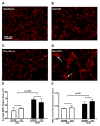
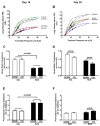
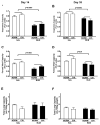
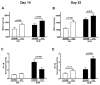
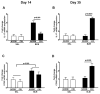
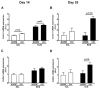
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) has been linked to increased mortality in pulmonary fibrosis. Its key feature, chronic intermittent hypoxia (CIH), can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation, known to lead to fibrotic pathology in other organs. We tested the effects of CIH in an animal model of bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis. Sprague Dawley rats were instilled intratracheally with bleomycin (Blm) or saline (Sal), and exposed to CIH or normal air (Norm) for 9 or 30 days. Pulmonary function was tested and lungs were harvested for histological and molecular analyses. In Blm-treated animals, 30days of CIH compared to Norm increased total lung collagen content (p=0.008) and reduced Quasi-static lung compliance (p=0.04). CIH upregulated lipid peroxidation and increased NF-κB activation, IL-17 mRNA and Col1α1 mRNA expression. Our results indicate that following Blm-induced lung injury, CIH amplifies collagen deposition via oxidative and inflammatory pathways, culminating in stiffer lungs. Thus, OSA may augment fibrosis in patients with interstitial lung disease.
Keywords: Fibrosis; Hypoxia; Intermittent; Lung/immunology/metabolism/pathology; Obstructive; Sleep apnea.
Published by Elsevier B.V.
Figures
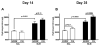
References
-
- Barrientos S, Stojadinovic O, Golinko MS, Brem H, Tomic-Canic M. Growth factors and cytokines in wound healing. Wound repair and regeneration: official publication of the Wound Healing Society [and] the European Tissue Repair Society. 2008;16:585–601. - PubMed
-
- Berend N. Protective effect of hypoxia on bleomycin lung toxicity in the rat. The American review of respiratory disease. 1984;130:307–308. - PubMed
-
- Borzone G, Moreno R, Urrea R, Meneses M, Oyarzun M, Lisboa C. Bleomycin-induced chronic lung damage does not resemble human idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. American journal of respiratory and critical care medicine. 2001;163:1648–1653. - PubMed
-
- Braun FM, Braun RK, Broytman O, Pegelow DF, Eldridge MW, Teodorescu M. LUNG INJURY, REPAIR, AND FIBROSIS: THE PLOT THICKENS FOR THREE’S COMPANY. American Thoracic Society; 2015. Chronic Intermittent Hypoxia Amplifies Oxidative Stress and Pulmonary Fibrosis Following Bleomycin-Induced Injury, A57; pp. A2080–A2080.
-
- Braun RK, Martin A, Shah S, Iwashima M, Medina M, Byrne K, Sethupathi P, Wigfield CH, Brand DD, Love RB. Inhibition of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis through pre-treatment with collagen type V. The Journal of heart and lung transplantation: the official publication of the International Society for Heart Transplantation. 2010;29:873–880. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

