Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae
- PMID: 28457352
- PMCID: PMC5412586
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cll.2017.01.005
Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacteriaceae
Abstract
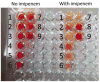
Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) have emerged as a major threat. Commonly used antibiotics are generally inactive against CRE. Therefore, timely detection of CRE is of paramount importance. Among CRE, those producing carbapenem-hydrolyzing β-lactamase enzymes (carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae) are particularly of concern because they tend to spread, and treatment is difficult. The carbapenemase groups most commonly encountered include KPC, NDM, and OXA-48. Treatment options are limited and include combinations of polymyxins, tigecycline, aminoglycosides, or carbapenems; newer agents with activity against CRE and better safety profiles are becoming available and will likely emerge as the preferred therapy.
Keywords: Carbapenemase; KPC; Rapid diagnosis.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Y.D. has served on advisory boards for Meiji, Achaogen, Allergan, Curetis, and has received research funding from The Medicines Company for a study unrelated to this work. A.I declares no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Epson EE, Pisney LM, Wendt JM, et al. Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae producing New Delhi metallo-β-lactamase at an acute care hospital, Colorado, 2012. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. 2014;35:390–397. - PubMed
-
- Lyman M, Walters M, Lonsway D, Rasheed K, Limbago B, Kallen A. Notes from the field: Carbapenem-resistant Enterobacteriaceae producing OXA-48-like carbapenemases--United States, 2010–2015. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2015;64:1315–1316. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease C, Prevention. Ten great public health achievements--United States, 1900–1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 1999;48:241–243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical