Anesthesia and perioperative pain management during cardiac electronic device implantation
- PMID: 28458575
- PMCID: PMC5402996
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S132241
Anesthesia and perioperative pain management during cardiac electronic device implantation
Abstract
Background: The degree of pain caused by the implantation of cardiac electronic devices (CEDs) and the type of anesthesia or perioperative pain management used with the procedure have been insufficiently studied. The aim of this study was to analyze perioperative pain management, as well as intensity and location of pain among patients undergoing implantation of CED, and to compare the practice with published guidelines.
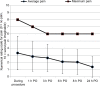
Patients and methods: This was a combined retrospective and prospective study conducted at the tertiary hospital, University Hospital Split, Croatia. The sample included 372 patients who underwent CED implantation. Perioperative pain management was analyzed retrospectively in 321 patients who underwent CED implantation during 2014. In a prospective study, intensity and location of pain before, during, and after the procedure were measured by using a numerical rating scale (NRS) ranging from 0 to 10 in 51 patients at the same institution from November 2014 to August 2015.
Results: A quarter of patients received analgesia or sedation before surgery. All the patients received local lidocaine anesthesia. After surgery, 31% of patients received pain medication or sedation. The highest pain intensity was observed during CED implantation with the highest NRS pain score being 8. Some patients reported severe pain (NRS >5) also at 1, 3, 6, 8, and 24 hours after surgery. The most common pain locations were surgical site, shoulder, and chest. Adherence to guidelines for acute perioperative pain management was insufficient.
Conclusion: Patients may experience severe pain during and after CED implantation. Perioperative pain management was suboptimal, and higher doses of sedation and intensive analgesia are required. Guidelines for acute perioperative pain management and anesthesia during CED implantation should be developed.
Keywords: analgesics; cardiac electronic devices; guidelines; pain intensity; perioperative pain management; postoperative pain.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Herce B, Nazeyrollas P, Lesaffre F, et al. Risk factors for infection of implantable cardiac devices: data from a registry of 2496 patients. Europace. 2013;15(1):66–70. - PubMed
-
- Hill PE. Complications of permanent transvenous cardiac pacing: a 14-year review of all transvenous pacemakers inserted at one community hospital. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 1987;10(3 Pt 1):564–570. - PubMed
-
- Gadler F, Valzania C, Linde C. Current use of implantable electrical devices in Sweden: data from the Swedish pacemaker and implantable cardioverter-defibrillator registry. Europace. 2015;17(1):69–77. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources