Levosulpiride and Serum Prolactin Levels
- PMID: 28459037
- PMCID: PMC5367242
- DOI: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_555_16
Levosulpiride and Serum Prolactin Levels
Abstract
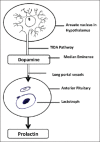
Levosulpiride is the levorotatory enantiomer of sulpiride used in dyspeptic syndromes of various etiologies. The prokinetic effect of levosulpiride is mediated through the blockade of enteric inhibitory dopaminergic type 2 (D2) receptors. The antagonism of central D2 receptors leads to both therapeutic (e.g. antiemetic effect due to D2 receptor blockade in the chemoreceptor trigger zone) and adverse (including hyperprolactinemia) effects. Dopamine is the main endogenous inhibitor of prolactin synthesis and secretion in the anterior pituitary. Levosulpiride causes significant elevation of serum prolactin levels in significant number of patients. The resultant hyperprolactinemia often manifests as distressing menstrual abnormalities and galactorrhoea in females. A significant number of patients who use levosulpiride develop serum prolactin levels of > 200 ng/mL that goes against the classical textbook teaching where pituitary tumor is supposed to be the mostly likely cause. Careful drug history in patients presenting with high serum prolactin levels will be of great help in reaching the exact diagnosis and avoiding unnecessary brain imaging.
Keywords: Galactorrhoea; hyperprolactinemia; levosulpiride.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
-
- Freeman ME, Kanyicska B, Lerant A, Nagy G. Prolactin: Structure, function, and regulation of secretion. Physiol Rev. 2000;80:1523–631. - PubMed
-
- Pan JT. Neuroendocrine functions of dopamine. In: Stone TW, editor. CNS Neurotransmitters and Neuromodulators: Dopamine. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1996. pp. 213–31.
-
- Manzanares J, Wagner EJ, LaVigne SD, Lookingland KJ, Moore KE. Sexual differences in kappa opioid receptor-mediated regulation of tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons. Neuroendocrinology. 1992;55:301–7. - PubMed
-
- Toney TW, Manzanares J, Moore KE, Lookingland KJ. Sexual differences in the stimulatory effects of bombesin on tuberoinfundibular dopaminergic neurons. Brain Res. 1992;598:279–85. - PubMed
-
- Moore KE, Demarest KT, Lookingland KJ. Stress, prolactin and hypothalamic dopaminergic neurons. Neuropharmacology. 1987;26:801–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources